Fork
Definition
This step is used to divide the workflow into two or more paths that will run in parallel, allowing multiple activities to run simultaneously.
/====> path 1 =====\
Fork ==== ==> Join
\====> path 2 =====/
Steps Tabs
Task details
This process type does not have task details for the fork step.
Incoming transitions
The Incoming transitions tab displays the previous steps where the flow comes from. When you create a process from a template or from scratch default incoming transitions are defined. It is allowed to customize the default setup, add new transitions, or delete transitions.
- From: the previous step, where the flow comes. Allows you to select where the workflow comes from.
- Incoming transition: brief name to identify the transition. That is the name of the action the form will show to the final user.
- To: current step.
- Action: allows creating a custom script to perform specific actions.
Example
Update custom attributes defined on metadata
userName = executionContext.getVariable("userName");
attributes = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserAttributes(userName);
newAttributes = new HashMap();
newAttributes.put("country", "FR");
language = attributes.get("language");
if (language == null) {
language = new LinkedList();
}
language.add("Spanish");
language.add("German");
newAttributes.put ("language", language);
serviceLocator.getUserService().updateUserAttributes(userName, newAttributes);Outgoing transitions
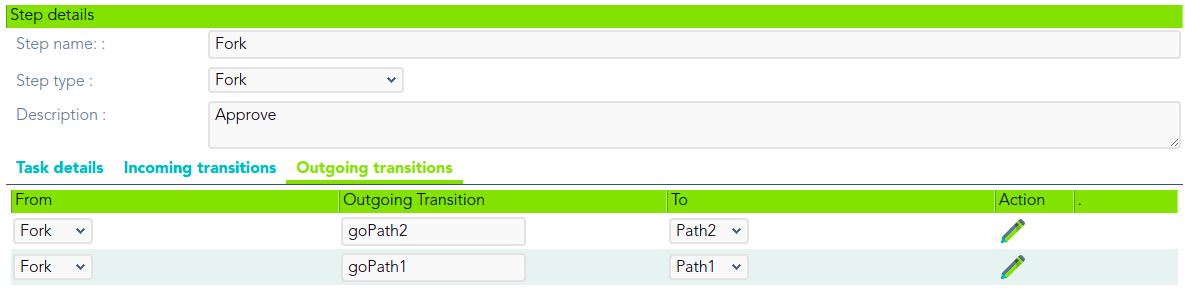
The Outcoming transition tab displays the next steps where the flow can go from the current step. When you create a process from a template or from scratch default outcoming transitions are defined. It is allowed to customize the default setup, add new transitions, or delete transitions.
- From: current step.
- Outgoing transition: name of the transition. It is a required field, you must comply it to the workflow run properly.
- To: the next step, where the flow goes.
- Action: allows creating a custom script to perform specific actions.
When you create an outcoming transition, Soffid creates the proper incoming transition.
Example
Scroll through the list of roles and the list of grant hierarchies to execute some actions.
userName = executionContext.getVariable("userName");
roleList = serviceLocator.getApplicationService().findRolesByUserName(userName);
for (role:roleList) {
//TO-DO
}
user = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserByUserName(userName);
roleGrantList = serviceLocator.getApplicationService().findRoleGrantHierarchyByUser(user.id);
for (roleGrant:roleGrantList) {
//TO-DO
}