SQL Connector
Introduction
Description
The SQL connector allows an easy way to configure and manage relational databases.
Managed System
There a lot of relational databases, currently these are the supported databases, but it's possible to include easily more systems
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- PostgreSQL
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Informix
- IBM DB2/400
For more information: List of relational databases
If your system is not in the previously list, it's possible to include it easily!
For more information to check if your system may be synchronized with this connector you do not hesitate to contact us through our Contact form
Prerequisites
It is needed a user with access and permissions to the schemes and tables required in the scope of the integration.
Download and Install
This addon is located in the Connectors section and its name is SQL plugin.
For downloadmore and install the addon you could review our generic documentationinformation about thisthe process: installation process you can visit the Addons installationGetting started page.
Agent Configuration
Basic
Generic parameters
After the installation of the addon, you may create and configure agent instances.
To configure this SQL connector you must select "Customizable SQL agent" in the attribute "Type" of the generic parameters section in the agents page configuration.
For more information about how you may configure the generic parameters of the agent, see the following link: Agents configuration
Custom parameters
Below there are the specific parameters for this agent implementation:
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
User name |
Database user name to authenticate |
|
Password |
Password of the database user |
|
Driver |
Identifies the driver of the relational database to use. Currently these are the supported databases: MySQL (& MariaDB), PostgreSQL, Oracle, MS SQL Server, Informix, DB2/400 |
|
DB URL |
URL that identifies the connection properties. Please refer to the specific database vendor documentation to build this URL |
|
Password hash algorithm |
Algorithm used to encrypt the password. For example SHA-1, SHA-256, MD5, etc |
|
Password hash prefix |
Algorithm used to encrypt the password. For example SHA-1, SHA-256, MD5, etc |
|
Enable debug |
Two options: "Yes", "No": it enables or not more log traces in the Synchronization Server log |
Attribute mapping
This connector can manage users, accounts, roles, groups and grants.
Properties
Any SQL sentence gets its parameters in a three step process:
- Synchronization engine creates the Soffid object.
- The Soffid object is translated into a managed system object, using the attribute translation rules.
- Soffid parser looks for any identifier preceded by a colon (:) symbol. For any symbol found, the symbol is replaced by a parameter whose value is the managed system attribute with the replaced identifier.
Once the SQL sentence has been executed, in case of SELECT clauses, the column names are used to generate a virtual managed system object. The last step is to apply the attribute translation to generate the Soffid object to be populated.
These are the properties required to map every object of the mapping:
|
Property |
Value |
|---|---|
|
selectAll |
SQL sentence that needs to be executed to retrieve all the objects that currently exists on the database.
|
|
check |
SQL sentence that will return when a single object already exists on the database |
|
insert |
SQL sentence to create a new object |
|
update |
SQL sentence to update an existing object |
|
delete |
SQL sentence to remove (or disable) an existing object |
|
selectByAccountName |
SQL sentence to gets user data based on the account name (for a single account information) |
|
selectByAccount |
SQL sentence to retrieve all the role grants made to an account (for a single account information) |
|
selectByName |
SQL sentence to fecth role information based on its name (for a single role information) |
|
selectByRole |
SQL sentence to retrieve all the accounts grantee of a role (used to update a role) (for a single role information) |
Attributes
You may map the attributes of the target system with the Soffid available attributes.
- For the target system attributes is required to be access to its specification
- For the Soffid attributes you may follow the next link
For more information about how you may configure attribute mapping, see the following link: Soffid Attribute Mapping Reference
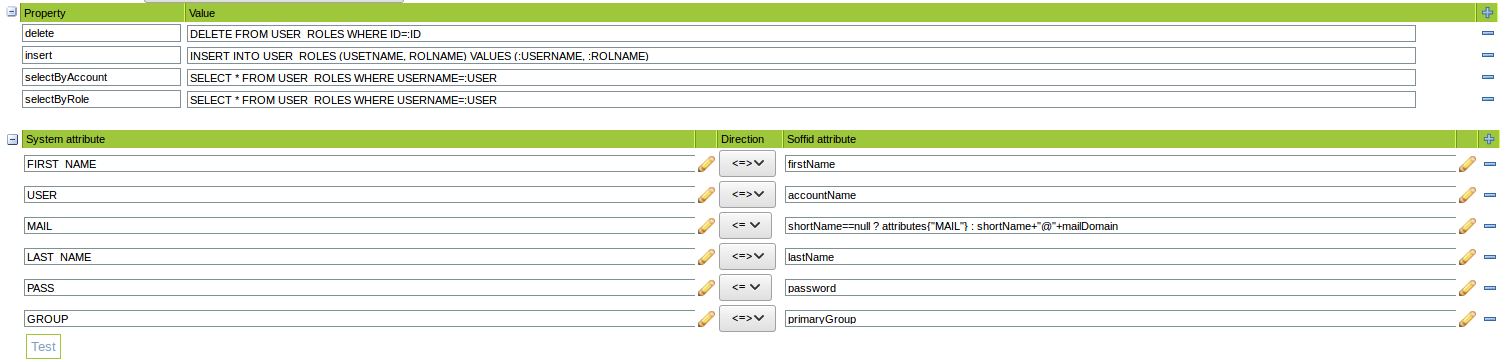
Example for roles:
Triggers
&&TODO&&Pending to be documented.
Load triggers
&&TODO&&Pending to be documented.
Account metadata
&&TODO&&Pending to be documented.
Operational
Monitoring
After the agent configuration you could check in the monitoring page if the service is running in the Synchronization Server, please go to:
Tasks
Authoritative
If you are checked "Authorized identity source", an automatic task to load identities from the managed system to Soffid is available, please go to:
And you will something like "Import authoritative data from <AGENT_NAME>".
Reconcile
If your are configured the "Attribute Mapping" tab with some of our objects: "user, account, role, group or grant", an automatic task to synchronize these objects from the managed system to Soffid is available, please go to:
And you will something like "Reconcile all accounts from <AGENT_NAME>".
Synchronization
About the synchronization of the objects, there are two possible options:
- If you are checked the generic attribute "Read Only" in the "Basics" tab, only the changes in the managed systems will be updated in Soffid. We recommend this options until the global configuration of Soffid will be tested.
- If you are not checked the generic attribute "Read Only" in the "Basics" tab, all the changes in Soffid or the managed system will be updated in the other. Note that this synchronization must be configured in the "Attribute mapping" tab correctly.
For more information about how you may configure the generic parameters of the agent, see the following link: Agents configuration