JSON REST Web Services Connector
Introduction
Description
This connector allows the integration with any Web Service able to consume and generate JSON documents through REST communication.
Managed System
Every commercial product or custom web application that allows REST communication with JSON documents.
There a lot of products that use this standard, for example:instance:
- JIRA.
- Oracle Filed Service Cloud (OFSC).
- Office 365.
- Dropbox.
If your system is not in the previouslyprevious list, it's possible to include it easily!
For more information to check if your system may be synchronized with this connector you do not hesitate to contact us us through our our Contact form
Prerequisites
It is needed a user with access and permissions to the endpoints and operations required in the scope of the integration.
Also the documentation, specification or tutorial of the implementation of the JSON REST Web Service is required to apply the mapping configuration.
Download and Install
This addon is located in the Connectors section and its name is REST (json) plugin.
For more information about the installation process you can visit the Addons Getting started page.
Agent Configuration
Basic
Generic parameters
After the installation of the addon, you may create and configure agent instances.
To configure this JSON REST Web Service Connector you must select "JSON Rest Webservice" in the attribute "Type" of the generic parameters section in the agents page configuration.
For more information about how you may configure the generic parameters of the agent, see the following link: Agents configuration
Custom parameters
Below there are the specific parameters for this agent implementation:
|
Parameter
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Server URL |
URL of the REST web service |
|
User name |
User to authenticate |
|
Password |
Password of the user to authenticate |
|
Authentication method |
Three options:
|
|
Authentication URL |
URL to retrieve the token for the authentication of the server (for "Token" method) |
|
Enable debug |
Two options: "Yes", "No": it enables or not more log traces in the Synchronization Server log |
| XML Templates |
Allows to add new XML templates with SOAP requests and then configure them at attribute mappings. |
Attribute mapping
This connector can manage users, accounts, roles, groups and grants.
Methods
This agent allows you to define methods to be called using the defined properties. There are some default methods, but you can customize your own methods.
Default methods:
- load
- delete
- update
- insert
- select
For each method, the properties to set up are as follows:
&&TODO&& Terminar
|
Properties
|
Description
|
|---|---|
| Path | A valid URL to call |
| Method | Available methods to call a Rest API (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH) |
| Encoding | Specific type of encoded data that will be used. |
| XML Template | |
| Parameters | |
| Success HTTP Codes | |
| Failure HTTp Codes | |
| Results | |
| Pagination URL | |
| Pagination script | |
| Condition script | |
| Optional header | |
| Optional header | |
| Optional header |
Properties
In this agent, the configuration of the properties attributes are very important due to they define the functionality of the integration:
This agent has five families of properties:
|
Family
|
Description
|
|---|---|
| Load | Used to retrieve all the |
| Select | Used to retrieve an |
| Insert | Used to create an object in the target system |
| Update | Used to update an object in the target system |
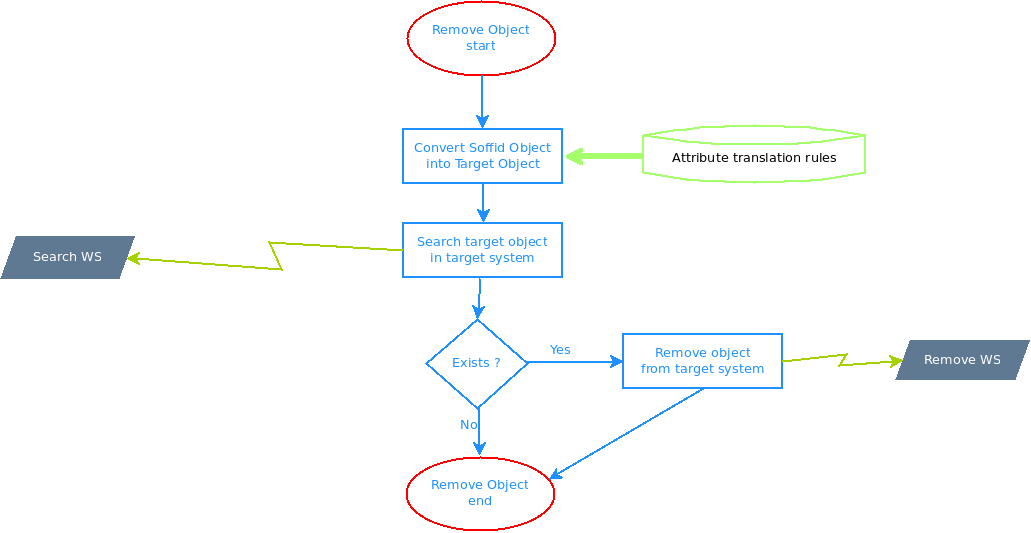
| Delete | Used to remove an object in the target system |
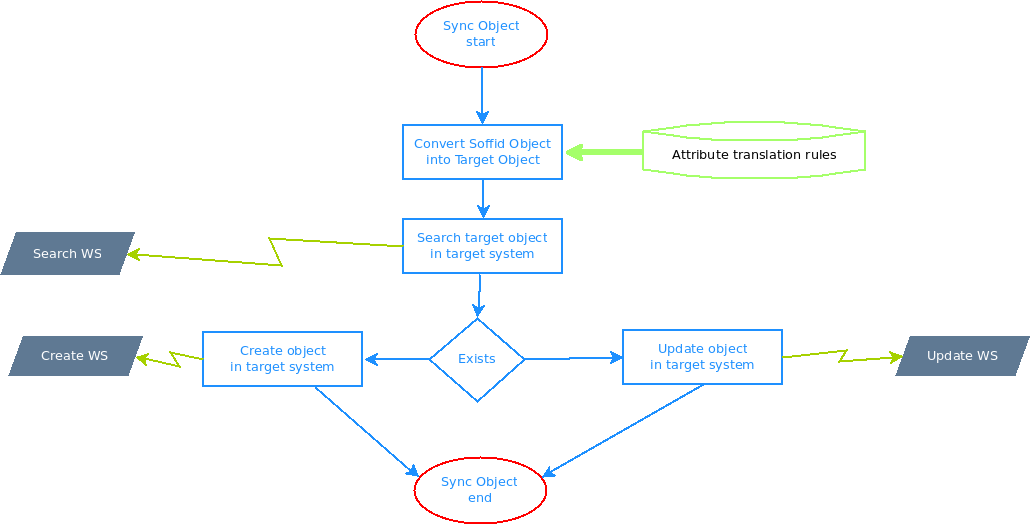
These families are involved in the following processes:
|
Process
|
Families
|
|---|---|
| Reconcile automatic task | Load + select |
| Authoritative automatic task | Load + select |
| Sync new object | Select + Insert |
| Sync updated object | Select + Update |
| Sync deleted object | Select + Delete |
These are the pictures of the mechanisms used to synchronize objects:
These are the properties attributes grouped by family:
Load
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Denotes the path (relative to webserver root) where the WebService is located. It can contain variable names in the form of ${variableName}. JSON connector will replace that name for the actual value. Eventually, complex expressions can be written in, but it's discouraged |
|
loadMethod |
Denotes the HTTP method to use: PUT, POST, GET and DELETE are allowed |
|
loadParams |
Put the character '-' in case you would avoid its value |
|
loadCheck |
Denotes a script that will check whether the invocation has been successful or not. Each JSON attribute received from the target WebService will be available as context variables |
|
loadResults |
But highly recommended) denotes the JSON portion that contains current data for the user. If this element is not present, or empty, the connector will conclude the user does not exist yet. This property will contain a simple JSON attribute name, but complex scripts are also allowed |
|
loadHeader |
Optional HTTP header(s) to send. More than one header can be sent by adding multiple propertis .....Header1, .Header2, and so on |
Select
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
selectPath |
Denotes the path (relative to webserver root) where the WebService is located. It can contain variable names in the form of ${variableName}. JSON connector will replace that name for the actual value. Eventually, complex expressions can be written in, but it's discouraged |
|
selectMethod |
Denotes the HTTP method to use: PUT, POST, GET and DELETE are allowed |
|
selectEncoding |
Denotes the encoding used to send to the target webservice. |
|
|
Denotes a script that will check whether the invocation has been successful or not. Each JSON attribute received from target web service will be available as context variables |
|
selectResults |
Denotes the JSON portion that contains current data for the user. It this element is not present, or empty, the connector will conclude the user does not exist yet. This property will contain a simple JSON attribute name, but complex scripts are also allowed |
|
selectHeader |
Optional HTTP header(s) to send. More than one header can be sent by adding multiple properties .....Header1, .Header2, and so on |
Insert
|
Property
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
|
Denotes the path (relative to webserver root) where the webservice is located |
|
insertMethod |
Denotes the HTTP method to use: PUT, POST, GET and DELETE are allowed |
|
insertEncoding |
Denotes the encoding used to send to the target webservice. |
|
insertCheck |
Denotes a script that will check whether the invocation has been successful or not. Each json attribute received from target web service will be available as context variables |
|
insertHeader |
Optional HTTP header(s) to send. More than one header can be sent by adding multiple properties .....Header1, .Header2, and so on |
|
insertParams |
Type in the attributes that will be sent to the rest server. If this property is not set, all attributes will be sent. |
Update
|
Property
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
|
Denotes the path (relative to webserver root) where the webservice is located |
|
updateMethod |
Denotes the HTTP method to use: PUT, POST, GET and DELETE are allowed |
|
updateEncoding |
Denotes the encoding used to send to the target webservice. |
|
updateCheck |
Denotes a script that will check whether the invocation has been successful or not. Each JSON attribute received from target web service will be available as context variables |
|
updateHeader |
Optional HTTP header(s) to send. More than one header can be sent by adding multiple properties .....Header1, .Header2, and so on |
|
updateParams |
Type in the attributes that will be sent to the rest server. If this property is not set, all attributes will be sent. |
Delete
|
Property
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
|
Denotes the path (relative to webserver root) where the webservice is located |
|
deleteMethod |
Denotes the HTTP method to use: PUT, POST, GET and DELETE are allowed |
|
deleteEncoding |
Denotes the encoding used to send to the target webservice. |
|
deleteCheck |
Denotes a script that will check whether the invokation has been successful or not. Each json attribute received from target web service will be available as context variables |
|
deleteHeader |
Optional HTTP header(s) to send. More than one header can be sent by adding multiple properties .....Header1, .Header2, and so on |
|
deleteParams |
Type in the attributes that will be sent to the rest server. If this property is not set, all attributes will be sent. |
|
preventDeletion (required) |
Set to false to enable delete method |
How to retrieve data from the response with the *Results properties
a) One level
If the JSON has one level you have to avoid the property
{
"userName" : "soffid"
}b) Two level
If the JSON has two levels you have to create the property *Result and put the name of the parent attribute, for example:
{
"user" : {
"userName" : "soffid"
}
}
And the property must be for example loadResults = userc) More than two levels
If the JSON has more than two levels you have to create the property *Result and put the atributes in the next pattern
*Results = attribure1{"attribute2"}{"attribute3"}...
For example:
{
"data" : {
"user" : {
"userName" : {
"string" : "soffid"
}
}
}
}
And the property must be for example:
loadResults = data{"user"}{"userName"}Attributes
You can customize attribute mappings, you only need to select system objects and the Soffid objects related, manage their attributes, and make either inbound and outbound attribute mappings.
You may map the attributes of the target system with the Soffid available attributes.
- For the target system attributes is required to be access to its specification.
- For the Soffid attributes, you may follow the next link.
For more information about how you may configure attribute mapping, see the following link: Soffid Attribute Mapping Reference
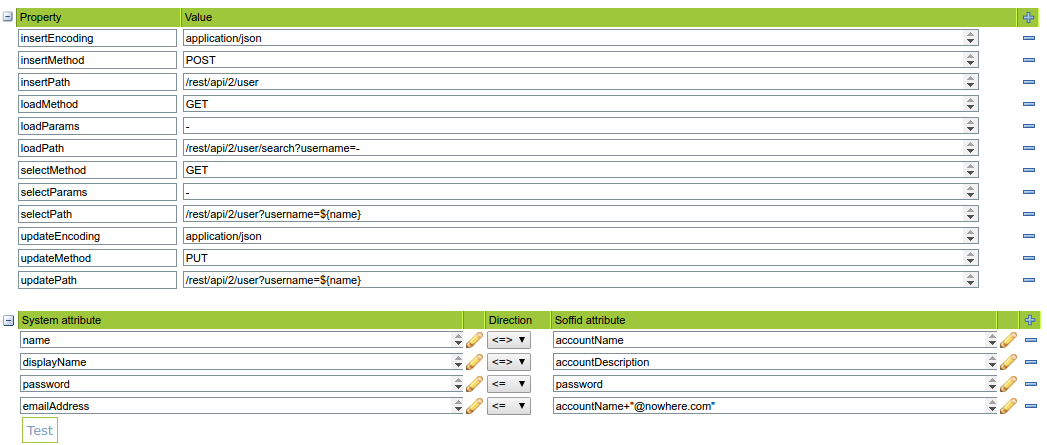
For example:instance:
As an example, below is how JSON connector will look like in order to manage JIRA accounts:
Triggers
You can define BeanShell scripts that will be triggered when data is loaded into the target system (outgoing triggers). The trigger result will be a boolean value, true to continue or false to stop.
Triggers can be used to validate or perform a specific action just before performing an operation or just after performing an operation into target objects.
To view some examples, visit the the Outgoing triggers examples page.
Load triggers
You can define BeanShell scripts that will be triggered when data is loaded into Soffid (incoming triggers). The trigger result will be a boolean value, true to continue or false to stop.
Triggers can be used to validate or perform a specific action just before performing an operation or just after performing an operation into Soffid objects.
To view some examples, visit the the Incoming triggers examples page.
Account Account metadata
Agents allow you to create additional data, on the "Account metadata" tab, to customize the accounts created for that agent. This additional information will be loaded with the agent's information, or calculated as defined in the mappings.
The additional data can be used in both mappings and triggers.
The attributes which you define here will be shown when you click on the proper account, on the Accounts Tabs at user page.
Operational
Monitoring
After the agent configuration you could check in the monitoring page if the service is running in the Synchronization Server, please go to:
Tasks
Authoritative
If you are checked checked "Authorized identity source", an automatic task to load identities from the managed system to Soffid is available, please go to:
And you will something like "Import authoritative data from <AGENT_NAME>".
Reconcile
If your are configured the "Attribute Mapping" tab with some of our objects: "user, account, role, group or grant", an automatic task to synchronize these objects from the managed system to Soffid is available, please go to:
And you will something like "Reconcile all accounts from <AGENT_NAME>".
Synchronization
About the synchronization of the objects, there are two possible options:
- If you are checked the generic
attributeattribute "Read Only" in the "Basics" tab, only the changes in the managed systems will be updated in Soffid. - If you are not checked the generic
attributeattribute "Read Only" in the "Basics" tab, all the changes in Soffid or the managed system will be updated in the other.
For more information about how you may configure the generic parameters of the agent, see the following link: Agents configuration