Textual Index
Introduction
A textual index is a data structure used in database systems to facilitate efficient search and retrieval of text-based information. It is designed to handle large volumes of textual data and provide quick access to relevant documents or records based on specified search criteria.
When a search query is performed on a database with a textual index, the index is queried to identify relevant documents or records that match the search terms. The index provides information about the location and relevance of the documents, which enables the database system to retrieve and present the results in a timely manner.
Textual indexes play a crucial role in enabling efficient search and retrieval of textual information in databases, making them an essential component in applications that handle large volumes of textual data, such as search engines, content management systems, and document repositories.
Soffid incorporates the textual index from version 3.5 using the Apache Lucene library.
Index configuration
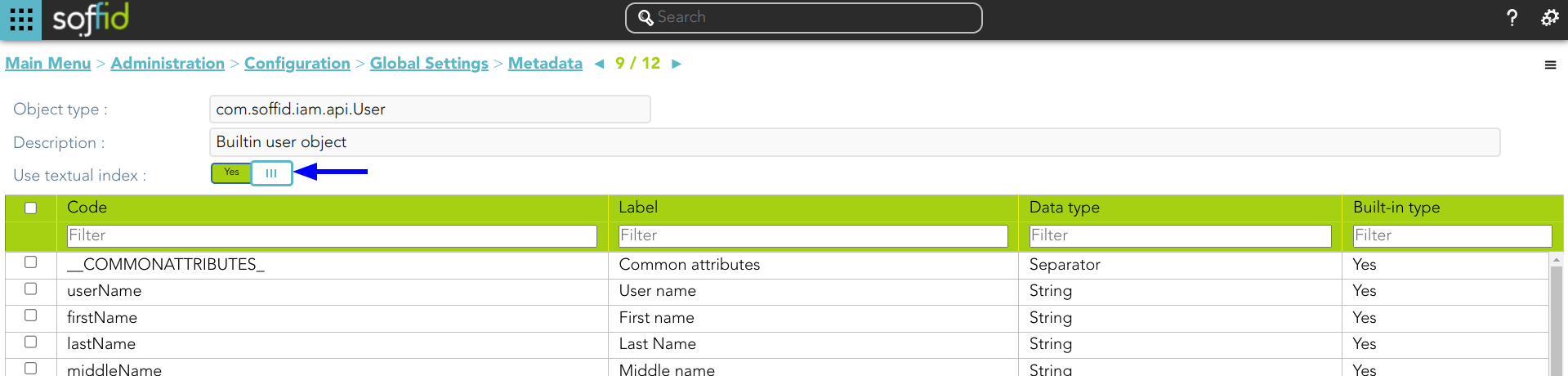
Soffid allows you to configure the objects you want to use in the textual index. To do this, you must select the proper object from the metadata page and enable the option "Use textual index". Once you enable this option, the textual index will be applied to the overall attributes of this object which have been included in the quick search
Example
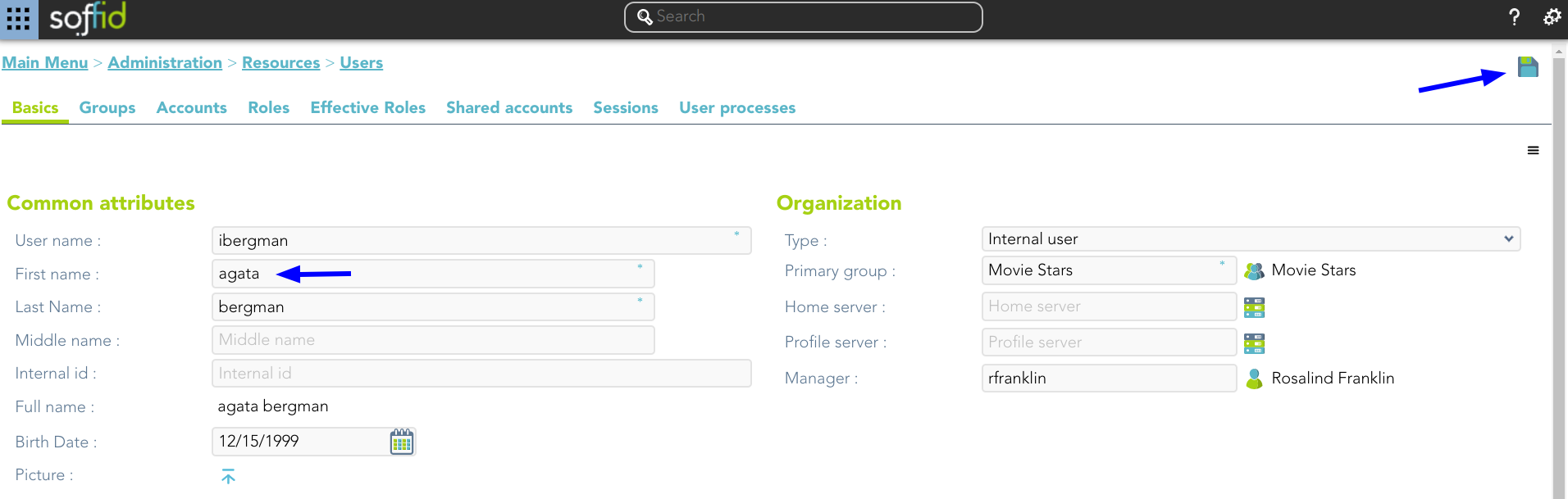
1. Enable the "Use textual index" on the User object and save the changes.
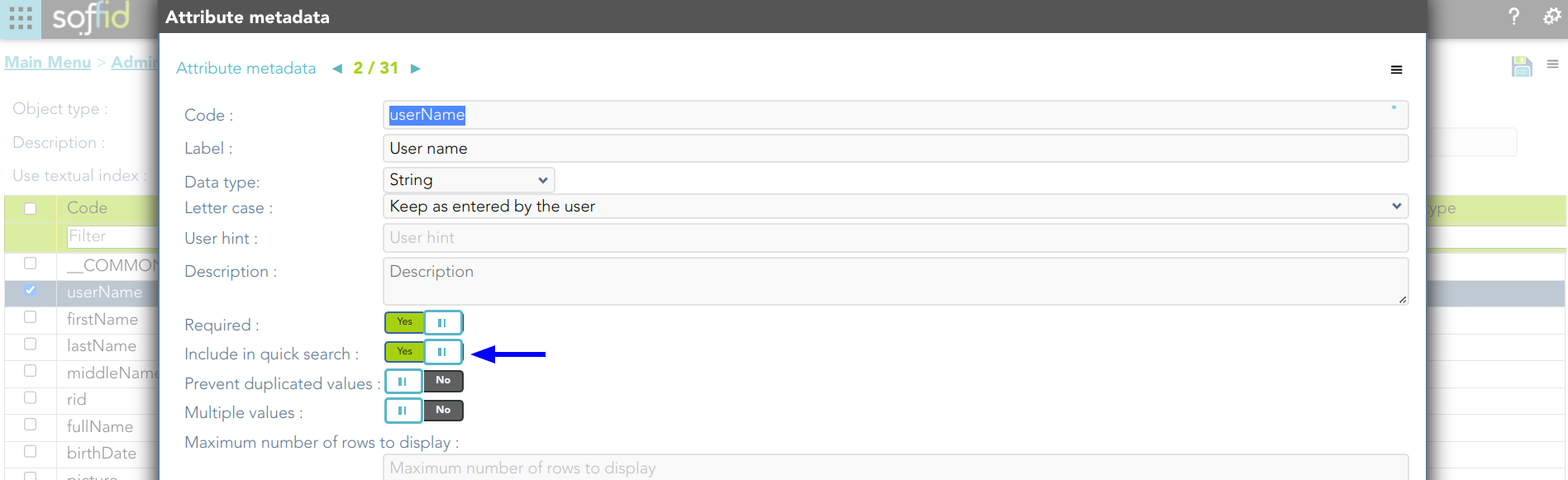
2. Check the attributes includes in the quick search.
How does the user interface search work?
Once you have configured the textual index for a specific object, Soffid will apply it when you use Quick Search on this object.
Example
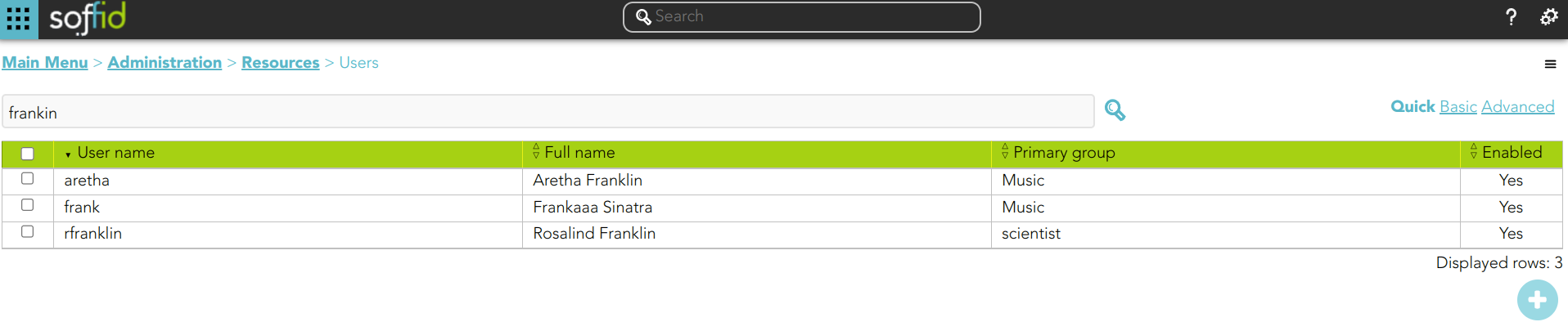
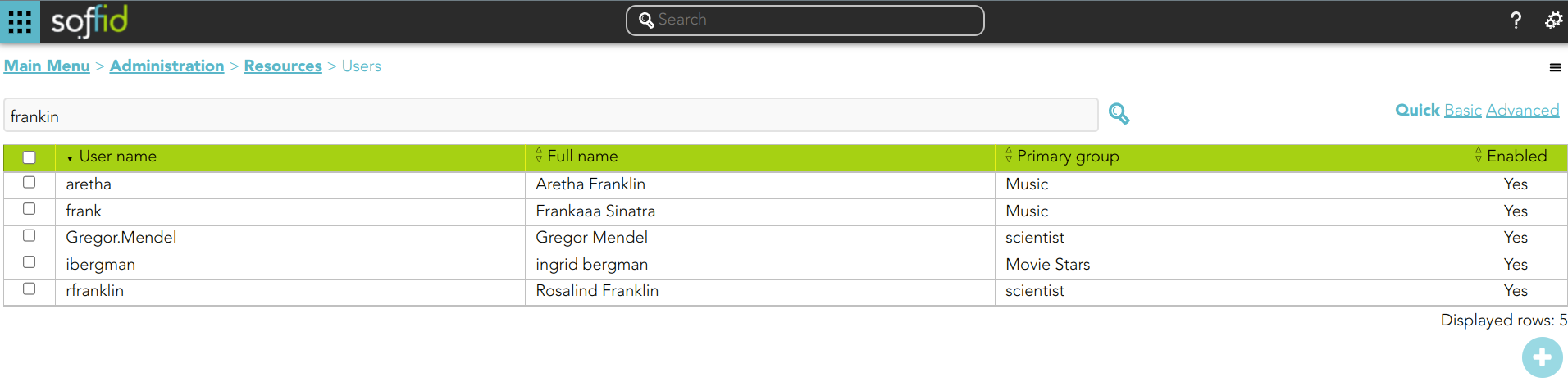
1. If you search for users using the text "frankin", then Soffid will display all the users whose userName, firstName, lastName, or middleName match with the typed text following the textual index rules.
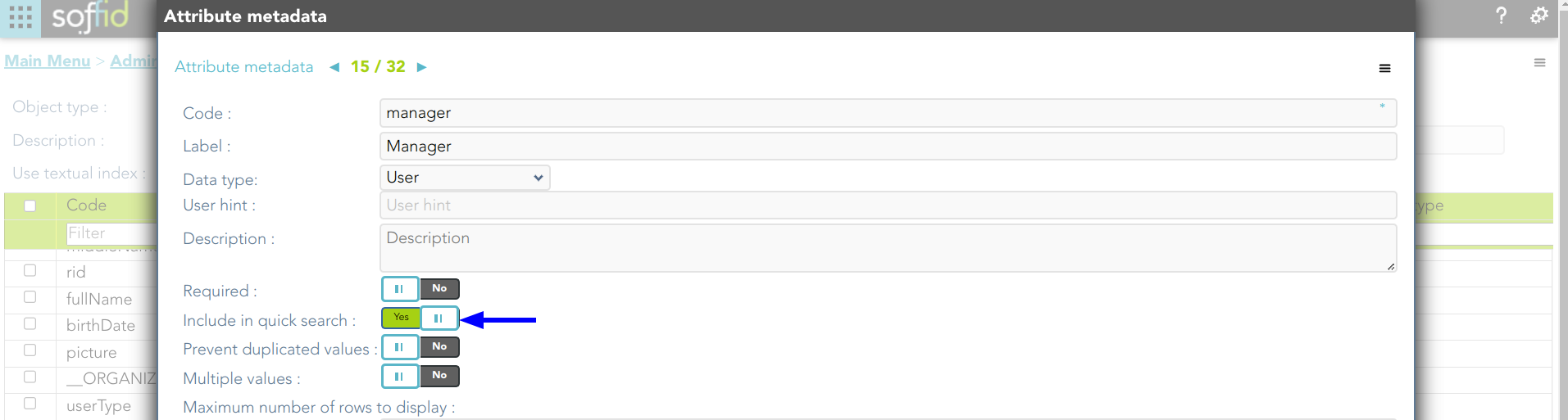
2.1. If you include the attribute manager in the quick search:
2.1. And search for "frankin", then Soffid will display all the users whose userName, firstName, lastName, middleName, or manager match with the typed text following the textual index rules.
How does SCIM interface search work?
1. First of all, you must install the SCIM addon in Soffid.
For more information, you can visit the How to install SCIM in Soffid? page.
2. Then, you can use any REST client to test and consume our SCIM REST web service.
For more information, you can visit the Testing tool page.
3. Finally, you can start to use the SCIM interface search by using Lucene syntaxis
Lucene syntaxis
Please browse the standard specifications in this link: https://lucene.apache.org/core/9_6_0/queryparser/org/apache/lucene/queryparser/classic/package-summary.html#package.description
Term Modifiers
Lucene supports modifying query terms to provide a wide range of search options. Here are the most common ones:
| Wildcard Searches |
To perform a single character wildcard search use the "?" symbol. To perform a multiple character wildcard search use the "*" symbol. |
| Regular Expression Searches | Lucene supports regular expression searches matching a pattern between forward slashes "/" |
| Fuzzy Searches | To do a fuzzy search use the tilde, "~", symbol at the end of a Single word Term |
| Proximity Searches | To do a proximity search use the tilde, "~", symbol at the end of a Phrase |
Boolean Operators
Example
1.
1.
1.
Operation
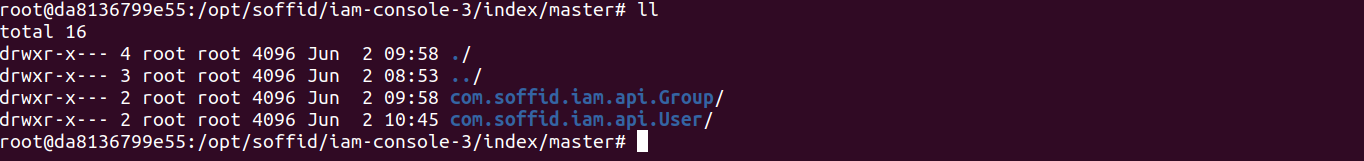
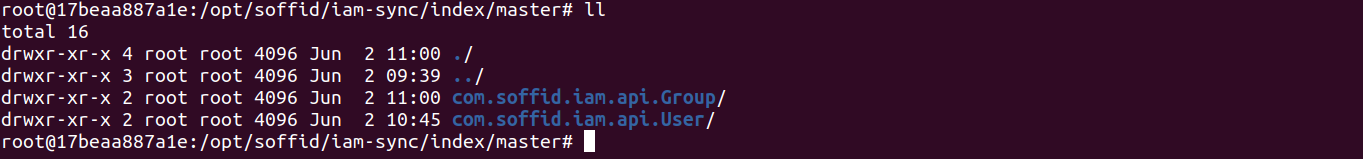
The Lucene index information is stored in files arranged in a folder structure. This folder structure is replicated in every Soffid Console and every Sync Server and also is saved in the database.
When you update an object, marked as the textual index, a task will be created. The soffid agent will execute this task and the Sync Server will update the database tables related to the textual index.
Folder structure
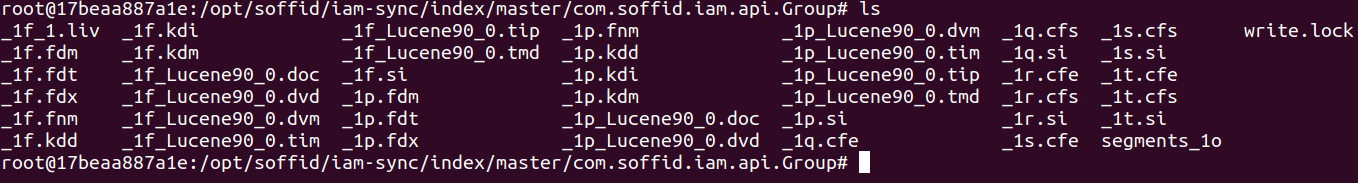
The folder structure is the following:
- ../index/<TENANT>/<SOFFID_OBJECT>
Example
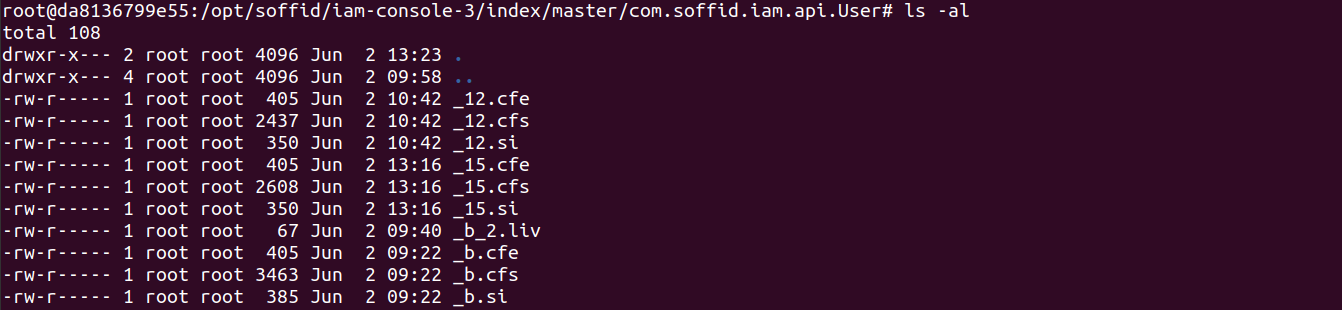
1. Here you are the folder structure for the Soffid Console
2. And the folder structure for the Sync Server
Database
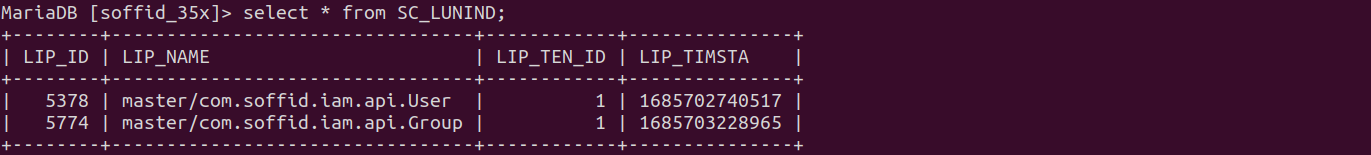
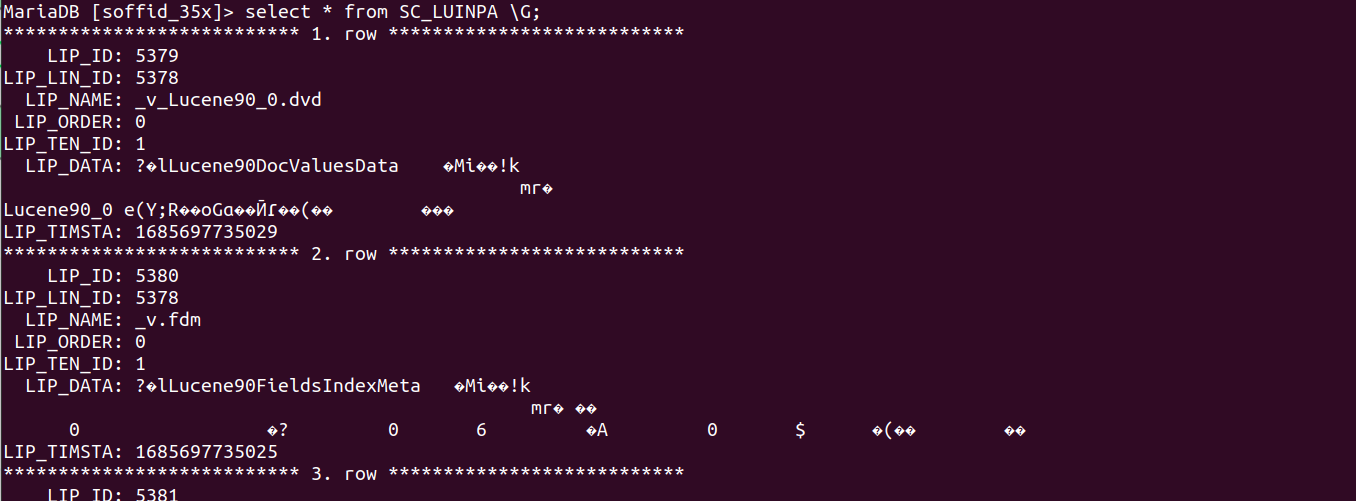
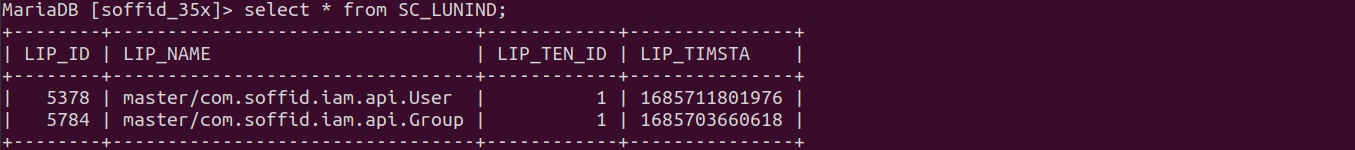
The database tables involved:
- SC_LUINPA
- SC_LUNIND
Example
1. The database structure
soffid agent
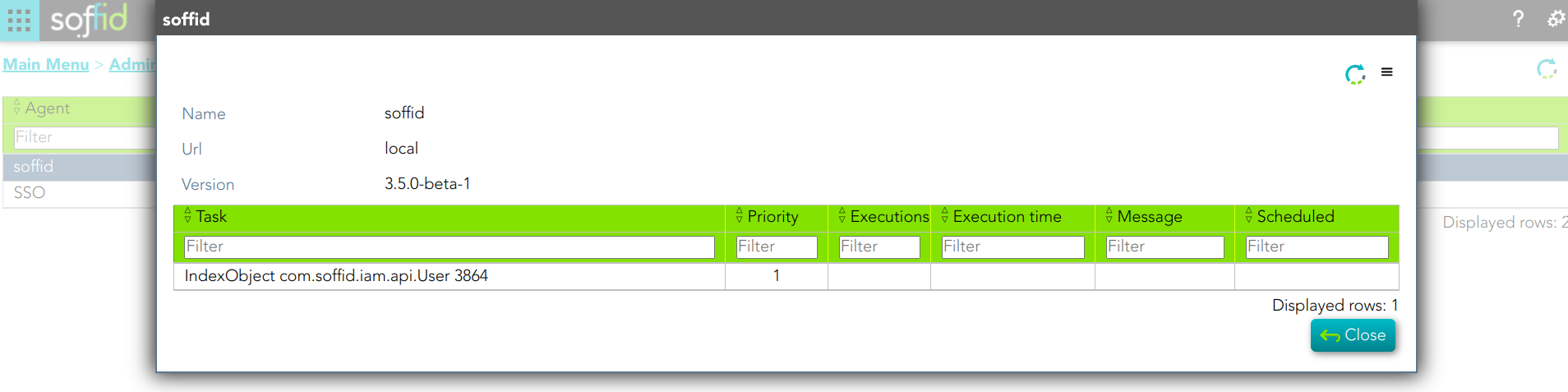
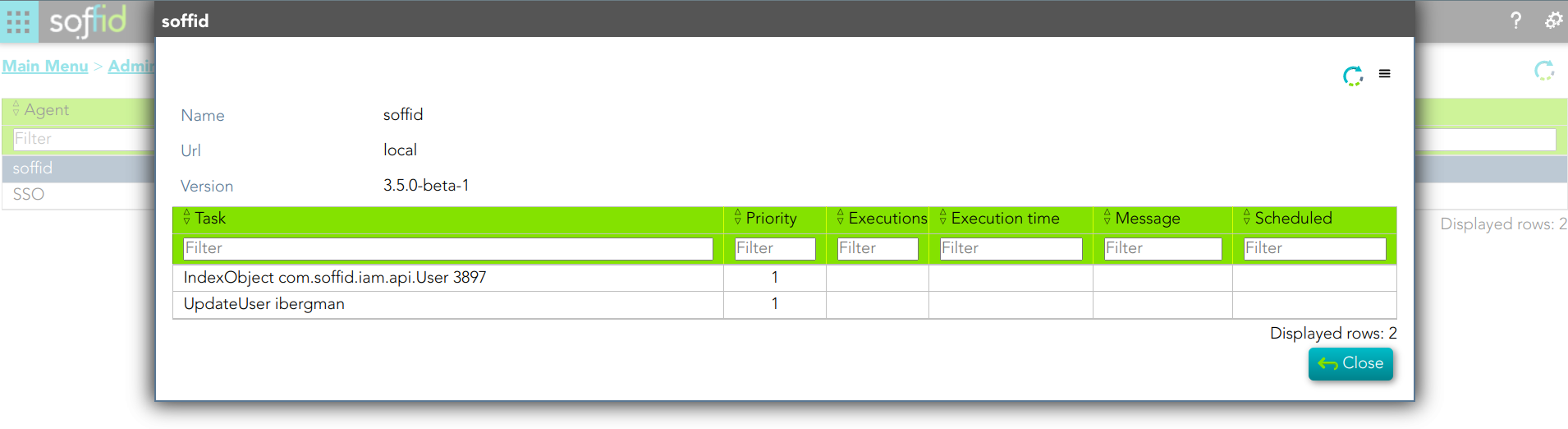
You can check the soffid agent status by visiting the Sync Server monitoring page:
Example
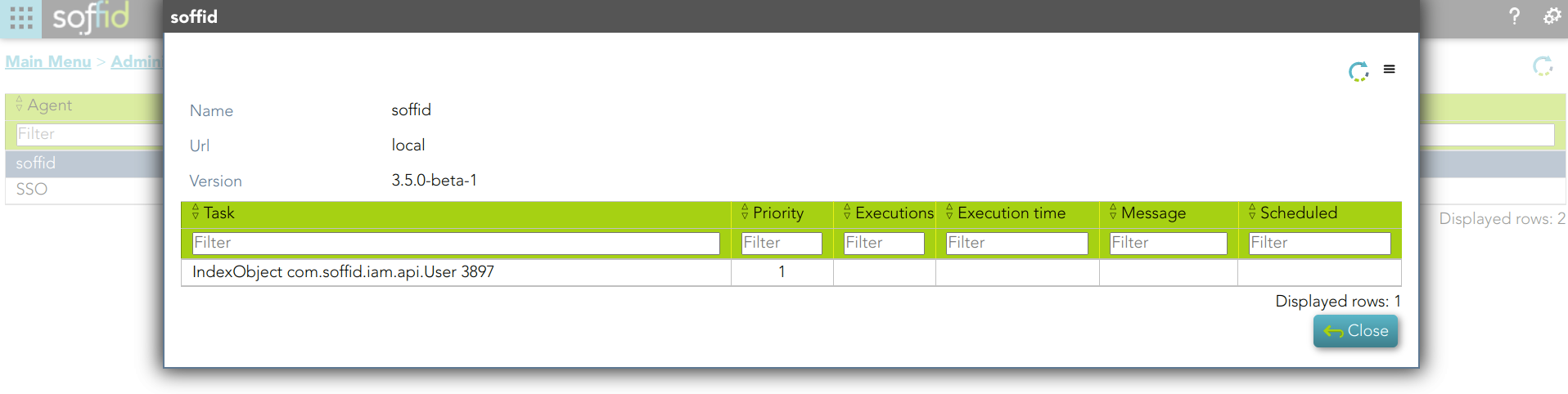
1. A soffid agent pending task:
Step-by-step
Example 1
1. You update one user's data and save the changes.
2. New tasks are created and executed.
3. Then Sync Server indexes the updated text and places the index file.
4. Then Sync Server and updates the database table SC_LUNIND by upgrading the LIP_TIMSTA field of the User object or by creating a new record if it did not previously exist.
5. When the following search will be performed, the very first thing to do is check the database file. If it is necessary update the file system and finally perform the search.
Example 2
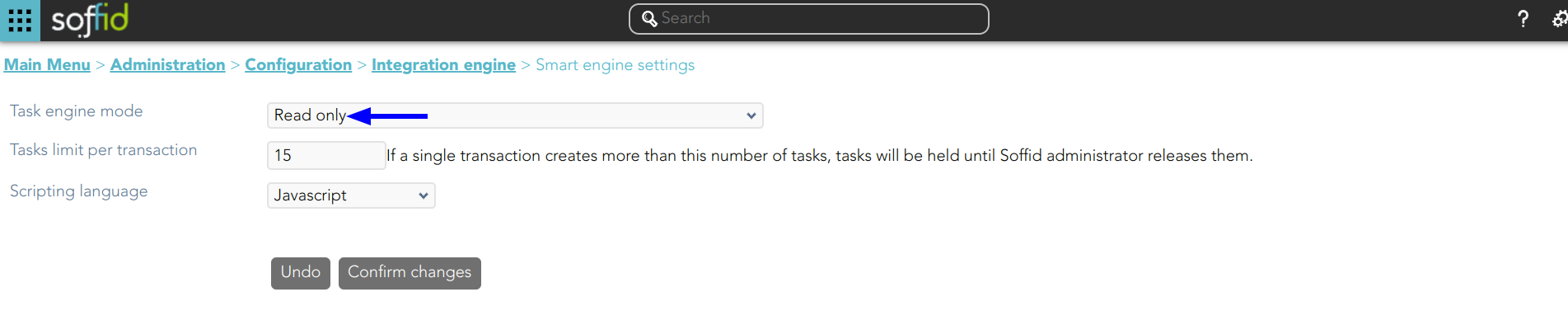
1. The task engine mode is Read only
2. You update one user's data and save the changes.
3. A new task is created and executed
4. Then Sync Server indexes the updated text and places the index file.
5. Then Sync Server and updates the database table SC_LUNIND by upgrading the LIP_TIMSTA field of the User object or by creating a new record if it did not previously exist.
6. When the following search will be performed, the very first thing to do is check the database file. If it is necessary update the file system and finally perform the search.