Connecting your custom applications
&&TODO&& pagina 46
Introduction
SAML 2.0 is a complex and not easy to implement standard. There are some libraries that can help somewhat, but a correct implementation needs a deep knowledge of SAML protocol, and is always hard to test and debug.
To make it easier, Soffid provides some JSON rest web services, that can help any application to correctly implement the SAML service provider part of the protocol.
Data flow
The following diagram, shows the resulting data flow between the end user, your application, the identity provider and Soffid web services:
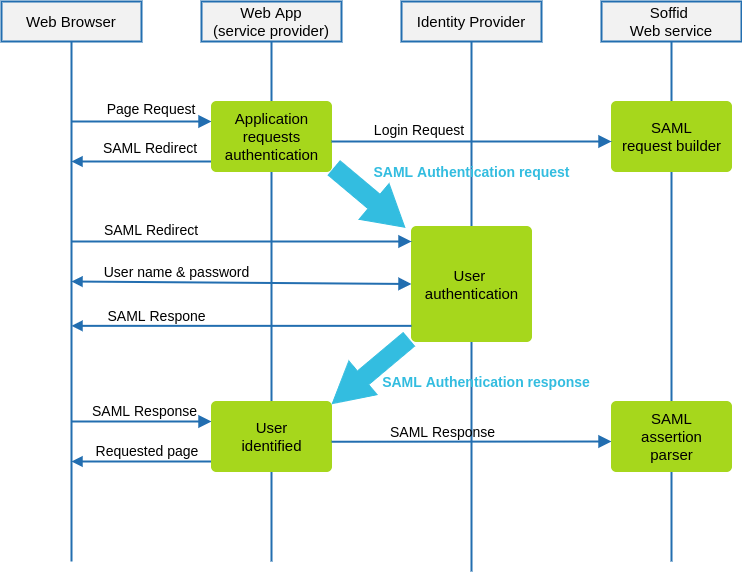
-
At the inital step, the end user requests access to a protected page.
-
The application can check the user identity looking up a session variable. By the time being, the user is not authenticated.
-
Your application issues a JSON request to Soffid web service. In turn, Soffid web service builds, signs and maybe encrypts a SAML request
-
Your application taks the JSOR request and builds an HTTP Redirect response with the received data.
-
The identity provider identifies the user as usual.
-
Your application receives the SAML response. At this point, your application packs and forwards the received data to Soffid Web Service.
-
Soffid Web Service decrypts and checks SAML response integrity and correctnes, and returns a JSON document specifying the success or failure status, and the underlying identity attributes. If needed, Soffid web service can provision a new identity in target systems on the fly.
-
Your application gets the identity data, stores it in a session variable and provides the protected resource to the end user.
In order to get it working, you must:
-
Declare your application as an internal service provider in federation page
-
Create a Soffid application account for your application.
-
Implement the protection filter
-
Implement the endpoint where SAML responses must be sent
