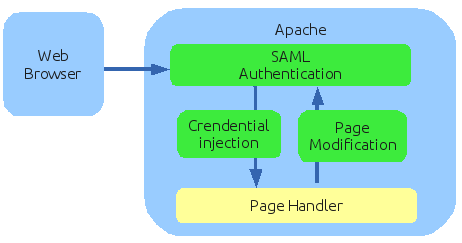
How web single sign-on works
Web Single Sign On acts introducing credentials to the underlying web application on behalf of the user. To perform its job, WSSO can:
-
Identify the user when needed
-
Modify pages generated by the web application in order to adapt them to the single sign on context.
- Pass credentials required to the web application.
- Close the web single sign on the session.
Phase 1. Page request
The user agent (actually the web browser), asks Apache for a web page.
If the ShibRequireSession tag is present at the web page location, Shibboleth will redirect the request to the configured Soffid SAML Identity Provider.
Phase 2. SAML Authentication
Soffid SAML Identity Provider will ask the user to identify itself. Depending on the federation configuration, the user will be allowed to:
-
Use certificate login
-
Enter username and password
-
Register itself
-
Recover the password.