Introduction to Identity Federation
What is Identity Federation?
A federated identity in information technology is the means of linking a person's electronic identity and attributes, stored across multiple distinct identity management systems.
It is related to single sign-on (SSO), in which a user's single authentication ticket, or token, is trusted across multiple IT systems or even organizations. SSO is a subset of federated identity management, as it relates only to authentication and is understood on the level of technical interoperability and it would not be possible without some sort of federation.
With the identity federeation we get to separate the applications and, the login and get permissions process. Currently, there are two mainstream identity federation standards: SAML and OpenID-Connect.
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language)
It is an identity federation protocol, born in 2001 and published in 2005. The design of SAML is highly secure and based on the technologies used at the beginning of this century. It uses XML tokens, signed and optionally encrypted using XMLdSig standard, and uses SOAP as its transport protocol.
SAML is an important component of many SSO systems that allow users to access multiple applications, services or websites from a single login process. SAML allows sharing security credential across systems.
SAML architecture
SAML is the most complete, secure and mature solution to get identity federation. SAML defines three main kind of servers:
- Federation metadata server. Publishes information about the federation members, its protocols and capabilities. Any federation member will only trust on other federation members.
- Identity providers are able to identify the user and publish its information to any application that requires it.
- Service providers are standard application servers that relays on identity providers to let users log in.
For now, we will focus on the single log-in and single log-out use cases, but be in mind that SAML defines much more use cases.
Use Cases
Single Log-in
The single log-in is usually initiated by the application server. The typical UML use case is as follows:
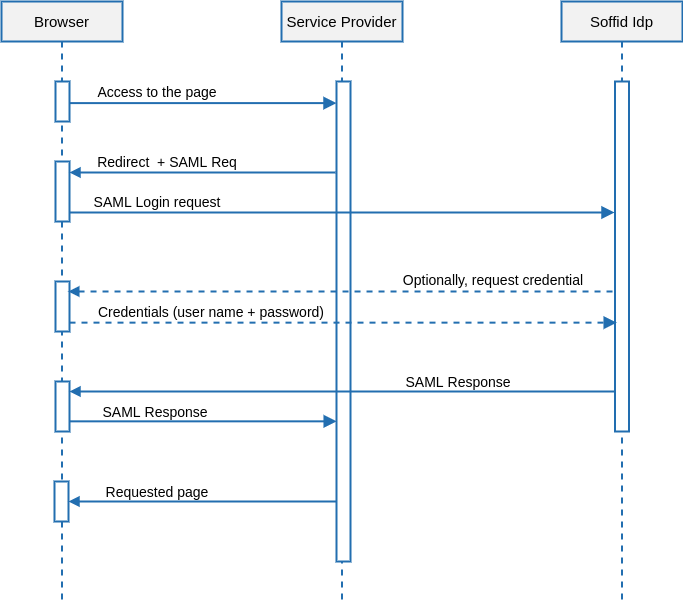

Single Log-out
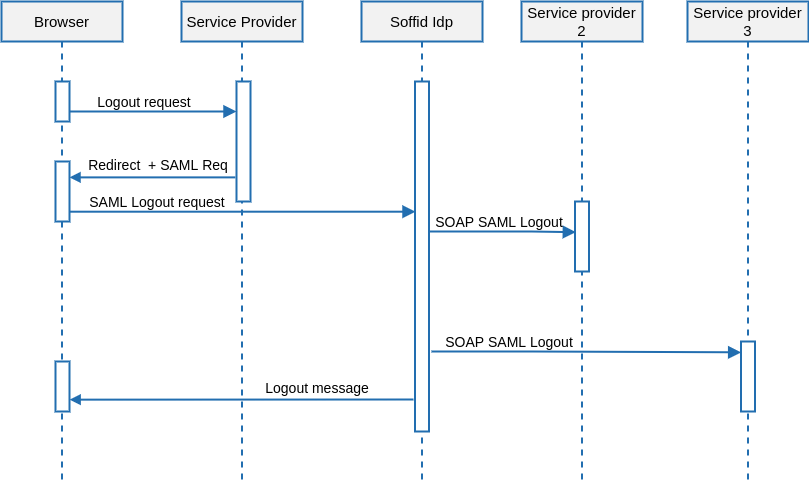

&&TODO&&
OpenID-Connect
OpenID-Connect is based on most modern protols. It uses JSON tokens, signed and optionally encripted using JWT standard, and uses simple REST as its transport protocol.
Sometimes referred as OpenID, must not be confused with an older and deprecated standard named OpenID.
OpenID architecture
Use Cases
Single Log-in
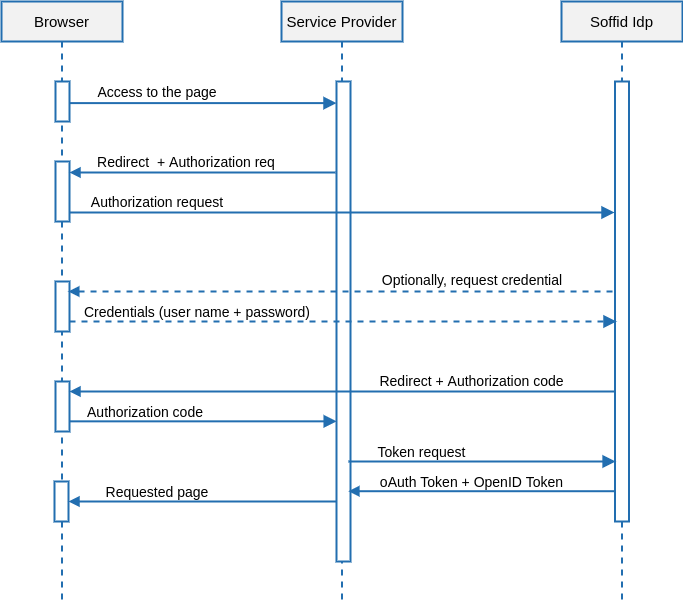
&&TODO&&
&&TODO&&
