Soffid offers a set of sample scripts. You can find examples visiting [the Sample scripts page](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/administration-scripting/page/sample-scripts).
Additionally, in the initial configuration of the container, we can configure the SOFFID\_TRUSTED\_SCRIPTS environment variable to allow the use of insecure classes. You can find this information visiting [the Installing IAM Console page](https://bookstack.soffid.com/link/27#bkmrk-4.-installation).
### Tips ##### Use the task engine mode for these scenarios: - **Read Only**: use this option after the Soffid installation until you have at least one target system configured to test the synchronization. - **Manual**: use this option for testing environments, or at the beginning of a live release. - **Automatic**: use this option for live environments, or also for the testing environments when the platform is mature. ##### Tasks limit per transaction: - Use a high task limit when you are comfortable with the configured processes of Soffid, for instance, 1000 or 10000 depending on the number of accounts of these external systems. ## Actions| **Confirm changes** | Allows you to update the engine settings. |
| **Undo** | Allows you to cancel the changes made and not confirmed. |
Soffid agents are the tool that allows the connection between the Soffid console and the target systems. To establish the connection with target systems, Soffid provides a large number of connectors that will be able to set up into the Soffid console.
You could see the complete list of [Synchronization Server Connectors](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors "Connectors").
Soffid administrator has the chance to easily customize attribute mappings for some connectors addons, without having to code it using Java. Soffid provides a graphical interface to perform attribute mapping. An agent will appear disabled when this agent won't have a server assigned. Bear in mind to select the “Disabled” flag on Server URL criteria when you will query if you want to search for disabled, but defined agents. ## Related objects 1. [**Synchronization server**](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/synchronization-servers "Synchronization servers") 2. [**Account naming rules**](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/account-naming-rules "Account naming rules") 3. [**User type**](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/user-type "User Type") 4. [**Password policies**](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/password-policies "Password policies") ## Standard attributes ### Basic - **Task engine mode**: shows the current task engine configuration. For more information visit the [Smart engine settings](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/smart-engine-settings "Smart engine settings") page. - **Name:** agent's identifying name. - **Description**: a brief description of the agent. - **Usage**: identify whether the accounts created are to be used for IAM or PAM. The IAM and PAM tasks will be managed in separate queues. *This attribute will be available in Soffid 3.5.10 or higher.* - **IAM** - **PAM**: - The PAM accounts will be managed as a Shared thread internally. - The PAM accounts will be shared accounts and never will be single user accounts. - **Type**: Identify the connector type to use. Different implementations of the server plugins are included in the connectors installed into Soffid. Each type has a Java class bound, the name of the Java class implementing the connector is displayed next to the connector name. - **Server**: synchronization will be performed with the selected server. It is allowed to select two servers in cases high disponibility will be necessary. If you choose two servers, when one fails, the other will be used. - If “*Each main synchronization server*” is selected, the agent will be run by every sync server. - If *"-disabled-"* is selected, the agent will be disabled. - If you select a single sync-server, the agent only will be run on that server. - **Shared Thread**: if it is enabled, the same thread will be shared to several synchronization servers. - **Dedicated Thread**: if "Shared thread" is disabled, it will be available the option to choose the number of threads to dedicate to the synchronization process. - **Task timeout (ms)**: add a timeout to the synchronization server tasks (query, insert, update, delete, update password, etc). If you add a timeout, when the connection gets this timeout, the synchronization server will stop the request and add it to the queue for a new retry later. - **Long task timeout (ms)**: add a timeout to the reconciliation server tasks (user, group, role, account, grants, etc). If you add a timeout, when the connection gets this timeout, the synchronization server will stop the request (no retry is added). - **Trust passwords**: check if you can trust it to propagate their passwords to Soffid. Trusted password agents differ from the non-trusted ones in: - Temporary passwords generated from the console only propagate to agents that have trusted passwords checked. In the other case, the agents only receive definitive passwords. - When a password has reached its expiry date, it will automatically be disabled on agents where the trusted password is not checked, so the user can no longer access it. - When the managed system detects a change in the user request password, the password will be propagated to Soffid only if the agent associated trusted password is checked. - If you want to forward the authentication requests to trusted target systems, you must enable the Trust passwords option and the proper feature on the [Authentication page](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/authentication "Authentication"). - **Authoritative identity source**: check if the agent will be used as the source for users' information. It is usually checked for the first load of users into Soffid, and then it is unchecked, being Soffid that manages users. Optionally, you can select a custom workflow to process incoming changes. - **Read-only**: if it is checked (the selected option is Yes), no change will be applied to the managed system. Only read operations will be allowed. - **Paused task**: if it is checked (the selected option is Yes), the system remains connected, but the tasks in the queue will be retained. It is very useful when conducting tests and ensuring that no tasks propagate, except the ones we are manually triggering (we pause, make the changes, and when everything is fine, we remove the pause). As a rule, you should pause when making configuration changes in production. - **Manual account creation**: - If you check NO, Soffid will create the new user accounts applying the defined policies. - Check YES if you don't want Soffid to create automatically new accounts for the users. - **Role-based**: when "Manual account creation" is not checked (option selected is No), it will show "Role-based". Check it if only users with any role on this agent should be created. When the identity or account loses its permissions, the account will be disabled. Uncheck to allow users with no role on it. - **Groups**: when "Manual account creation" is not checked (option selected is No), it will show "Groups". Identify the business units that are allowed to have an account on this system. - **User domain**: it is the rule used to determine how to generate account names. If the account name is the same as the user name (as is normally the case), the “Default user domain” should be used. The user domain values are defined on the [Account naming rules](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/account-naming-rules "Account naming rules") page. - **Password domain**: determines the password policies that will be used. If the "Default password domain" is selected, Soffid passwords will be shared with the managed systems. The user domain values are defined on the [Password policies](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/password-policies "Password policies") page. - **User Type**: when "Manual account creation" is not checked (option selected is No), it will show User Type. Only users of the selected types will be created. Any change made in this field involves all accounts to be recalculated. New ones will be added to the repository and managed systems. Some accounts will get disabled if the owner user no longer belongs to any authorized user type.When uploading authoritative data for identities from a managed system, firstly, users will be created in Soffid as indicated in the attribute mapping, and secondly, accounts will be created for the managed systems only if the agent option "Manual account creation" is not checked and only for User Types indicate.
#### Connector parameters The custom attributes depend on the used plugin. Here you will find all the information needed about the available Soffid connectors to integrate external managed systems. 1. [AWS Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/aws-connector "AWS Connector") 2. [CSV Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/csv-connector "CSV Connector") - [Customizable CSV file (CSV Connector type)](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors/page/customizable-csv-file-csv-connector-type "Customizable CSV file (CSV Connector type)") 3. [Google Apps Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/google-apps-connector "Google Apps Connector") 4. [JSON REST Web Services Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors/chapter/json-rest-web-services-connector "JSON REST Web Services Connector") 5. [LDAP Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/ldap-connector "LDAP Connector") 6. [Oracle Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/oracle-connector "Oracle Connector") 7. [Oracle EBS Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/oracle-ebs-connector "Oracle EBS Connector") 8. [SAP Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/sap-connector "SAP Connector") 9. [SCIM Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/scim-connector "SCIM Connector") 10. [Shell Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/shell-connector "Shell Connector") - [Invoker interface](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors/page/invoker-interface "Invoker interface") 11. [SQL Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/sql-connector "SQL Connector") 12. [Windows Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/windows-connector "Windows Connector") - [HOWTO SSL access to Active Directory](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors/page/invoker-interface "Invoker interface") - [Invoker interface for Active Directory](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors/page/invoker-interface-for-active-directory-skip-to-end-of-metadata "Invoker interface for Active Directory Skip to end of metadata") 13. [Zarafa Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/zarafa-connector "Zarafa Connector") 14. [SQL Server Connector](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors/page/sql-server-connector) ### Integration flows Some connector addons have associated integration workflows. On the Integration flows tab you can view the integration flows related to the agent. You also can view in detail the workflows and test them. ### Attribute mapping The attribute mapping tab only appears when the agent allows such customization. Soffid administrators have the chance to easily customize attribute mappings without having to code them using Java. The administrator users can select system objects and the Soffid objects related, manage their attributes, and make either inbound and outbound attribute mappings. There is an action that creates all the default mapping depending on the agent connector type. That option creates automatically system objects with their attributes and properties, you can select them by clicking on the hamburger icon and then the **Create default mapping** option. Once created the default mapping, those can be customized as required. #### Properties Some agents require to configure some custom attributes in their properties section. These properties are specific for each type of connector. You could see all these properties by visiting each connector type page. #### Methods This option is only available on some types of connectors. It is used to define methods that can be called using the defined properties. #### Attributes Each object mapping defines an agent object name and one bound Soffid object type. The left hand side attributes are managed system attributes, so they are agent dependent that is being configured. The right side attributes are Soffid attributes and must be selected from an existing list.It is allowed to use bean Shell expression in the source when the mapping is one-way.
##### System attributes A configuration agent must define object types that can be created on it. Each object mapping defines an agent object name and needs bound Soffid object type. At this column, the system's attribute name will be displayed. When evaluating any expression, either the system or soffid attributes are available as script variables. Moreover, the following variables are available:| **Variable** | **Content** |
| serverService | Server API that enables an easy object query \[ Search the link "Public API Module" or "Data & Service model" \] |
| serviceLocator | Spring Singleton that gets access to any published service bean. Only available on the main syncserver |
| remoteServiceLocator | Singleton that gets access to any remotely published service bean. |
| THIS | HashMap that contains any soffid or system managed attribute. It can be used when the attribute name is not a valid java identifier. |
| [dispatcherService](https://bookstack.soffid.com/link/75#bkmrk-dispatcherservice) | Service that allows the script to get or update information in the target system. |
| **System attribute** | **Direction** | **Soffid attribute** | **Meaning** |
| cn | <=> | accountName | The account name is the CN attribute of the LDAP |
| departmentNumber | <= | ```javascript for (group: secondaryGroups) { if (group.get("name").equals(primaryGroup)) { return group.get("description"); } } return null; ``` | Assigns the group description of the primary group to the departmentNumber attribute |
| baseDN | => | "ou="+primaryGroup+",dc=soffid,dc=org" | Assigns the base dn of the user to the proper organization unit that is below dc=soffd,dc=org. |
| **Variable** | **Content** |
| serverService | Server API that enables an easy object query \[ Search the link "Public API Module" or "Data & Service model" \] |
| serviceLocator | Spring Singleton that gets access to any published service bean. Only available on the main syncserver |
| remoteServiceLocator | Singleton that gets access to any remotely published service bean. |
| THIS | HashMap that contains any soffid or system managed attribute. It can be used when the attribute name is not a valid java identifier. |
| [dispatcherService](https://bookstack.soffid.com/link/75#bkmrk-dispatcherservice) | Service that allows the script to get or update information in the target system. |
| **Trigger** | |
| preInsert | It will be triggered just before the insert action. It will be used to validate or prevent the insert action, and also to prepare objects or actions when a new object will be inserted |
| preUpdate | It will be triggered just before the update action. It will be used to validate or prevent update an object. |
| preDelete | It will be triggered just before the delete action. It will be used to validate or prevent delete an object. |
| postInsert | It will be triggered just after the insert action. It will be used to trigger or prevent an action. |
| postUpdate | It will be triggered just after the update action. It will be used to trigger or prevent an action. |
| postDelete | It will be triggered just after the delete action. It will be used to trigger or prevent an action. |
| preSetPassword | It will be triggered just after the set password action. It will be used to trigger or prevent an action. |
| postSetPassword | It will be triggered just after the set password action. It will be used to trigger or prevent an action. |
For more examples, you can visit the [Incoming Triggers examples page](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors/page/incoming-triggers-examples).
### Load triggers On the Load trigger tab, it is allowed to set up a specific configuration for the agent and define BeanShell or JavaScript scripts that will be triggered when data is loaded into Soffid (**incoming triggers**). - **Full reconciliation**: switch off to enable incremental load process and disable Soffid object removal. - **Propagate changes**: switch off to prevent sync-server to create synchronization tasks after loading incoming changes. To add a new trigger, it is mandatory first of all, to select a Soffid object on which the action will be performed. Then to select the trigger, that determines the moment at which the script will be triggered. Finally, define the BeanShell script that will be executed. The available objects are the following: - User - Account - Group - Role - Grant Triggers can be used to validate or perform a specific action just before performing an operation or just after performing an operation into Soffid objects. **The trigger result will be a boolean valu**e, true to continue or false to stop. In a Load Trigger, it is not possible to access to mapping definitions configured on the attribute mapping tab. It will be necessary to use **newObject{"attributeName"}** to get the new value, or **oldObject{"attributeName"}** to get the old value. Those objects will be in Soffid format.For more info about the Soffid format, you can visit the [Soffid Objects page](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/soffid-objects).
| **Trigger** | |
| preInsert | It will be triggered just before the insert action. It will be used to validate or prevent the insert action. |
| preUpdate | It will be triggered just before the update action. It will be used to validate or prevent update an object. |
| preDelete | It will be triggered just before the delete action. It will be used to validate or prevent delete an object. |
| postInsert | It will be triggered just after the insert action. It will be used to trigger or prevent an action. |
| postUpdate | It will be triggered just after the update action. It will be used to trigger or prevent an action. |
| postDelete | It will be triggered just after the delete action. It will be used to trigger or prevent an action. |
For more examples, you can visit the [Outgoing Triggers examples page](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors/page/incoming-triggers-examples).
### Massive actions Massive Actions refer to bulk or large-scale operations that can be performed across multiple identities, accounts, or resources managed by an agent within the Soffid platform. Agents in Soffid are components responsible for interacting with external systems (like directories, databases, or applications) to manage and synchronize identity-related data. Massive actions allow administrators to execute operations on a large number of items simultaneously, making it easier to manage and maintain the system efficiently. #### Provisioning all users on to managed systems One of the main features of identity and access management (IAM) is automated user provisioning. User provisioning is the process that ensures the users are created, with proper permissions, updated, disabled, or deleted on to managed systems. All managed systems must have an agent configuration, which will determine the way to perform the provisioning. Soffid shows information about the last time that the option was run and a report with the details. You can access the report by clicking the verification icon (✓). #### Propagate groups to agent This option allows pushing to the managed system all the defined groups in Soffid. Soffid shows information about the last time that option was run and a report with the details. You can access the report by clicking the verification icon (✓). #### Reconcile (load target system objects) The main purpose of reconciling process is to provide a mechanism to ensure that all users are aligned on the specific roles and responsibilities. Reconcile process discovers new, changed, deleted, or orphaned accounts to determine user access privileges. Not every system connector has the capabilities needed to execute the reconcile process. When "Read only" property, in Basic parameters, is checked (selected value is Yes), the reconcile process only considers unmanaged accounts. Soffid shows information about the last time that the option was run and a report with the details. You can access the report by clicking the verification icon (✓). #### Load authoritative data for identities and groups Identities use to live on authoritative identity sources and they do in Soffid as well. Each identity may have any number of accounts on each managed system. When "Authoritative identity source" is checked (option selected is Yes) Soffid will show the option that allows the load authoritative data for identities and groups. That option performs the operations to **load data of groups and data of identities** from the managed system into Soffid, following the rules configured in the agent. Soffid shows information about the last time that the option was run and a report with the details. You can access to the report by clicking the verification icon (✓). Also, Soffid creates a parameter on the [Soffid parameters page](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/soffid-parameters "Soffid parameters"), with information about the version of the data. If you need to perform the load authoritative action, it will be mandatory to delete this parameter before perform the action. #### Generate target system potential impact That option allows you to generate a report with all the potential changes that would be performed on the managed system with the current agent configuration If that option was performed previously, Soffid will show information about the last time that the option was run and the report with the potential impact. You can access the report by clicking the verification icon (✓). ### Account metadata Agents allow you to create additional data, on the "Account metadata" tab, to customize the accounts created for that agent. This additional information will be loaded with the agent's information, or calculated as defined in the mappings. The additional data can be used in both mappings and triggers. To get the Account Metadata value, or to put value, you need to use **accountAttributes{"ATT\_NAME"}** #### Standard attributes - **Code**: short name used by scripts and connectors to access the underlying information. It is suggested to use short names without blanks or special characters to make it easier to use. - **Label**: text displayed just beside the attribute value. It is advised to use short descriptions in order to keep the screen cleaner. - **Data type**: The attributes can have different data types - **Prevent duplicated values**: mark this field as a unique key for the object type. There is no chance of two objects with the same attribute value. Soffid smart engine will avoid the creation of duplicated objects. - **Multiple values**: some attributes can contain multiple values for the same object. For instance, an attribute containing the languages a user can speak can be multi-valued, as a user can speak multiple languages. - **Maximum number of rows to display**: when an attribute is multivalued, the screen size can grow a lot. To prevent such a big form, the system will only display a maximum number of values, and a scroll bar will appear to browse through the attribute values. - **Size**: primarily for string attributes, specify the maximum length in characters of the attribute value. - **Values**: primarily for string attributes, you can specify the allowed values for the attribute. Then, the text box that the user has to fill in the data will be replaced by a drop-down list. - **Visibility expression**: write an optional BeanShell expression to check if the field should be displayed or not. The expression should return true or false. The following variables are exposed to the expression: - ownerObject: current object owning the attribute. - value: current attribute value. - requentContext: tip about the screen using the attribute. - inputField: the ZK input object (ZK Framework). - inputFields: a map to get access to any other ZK input object (ZK Framework). - serviceLocator: locator to use any Soffid engine microservice. - **Validation expression**: write an optional BeanShell expression to check if the field value is acceptable or not. The expression should return true if the value is acceptable. If the expression returns false or any other object, a warning message will be displayed. When the expression returns a string value, the return value will be considered the warning message to present to the end-user. The following variables are exposed to the expression: - ownerObject: current object owning the attribute - value: current value to evaluate. - requentContext: tip about the screen using the attribute - inputField: the ZK input object (ZK Framework). - inputFields: a map to get access to any other ZK input object (ZK Framework). - serviceLocator: locator to use any Soffid engine microservice. - **onLoad trigger**: write an optional BeanShell expression that will be executed just after preparing the user interface. The script can modify in any way the inputField object before it is displayed, but cannot modify other input fields. The following variables are exposed to the expression: - - ownerObject: current object owning the attribute - value: current value to evaluate. - requentContext: tip about the screen using the attribute - inputField: the ZK input object (ZK Framework). - inputFields: a map to get access to any other ZK input object (ZK Framework). - serviceLocator: locator to use any Soffid engine microservice. - **onChange trigger**: write an optional BeanShell expression that will be executed just after the user has changed the object value. The script can modify in any way the inputField object or any other input fields. The following variables are exposed to the expression: - - - ownerObject: current object owning the attribute. - value: current value to evaluate. - requentContext: tip about the screen using the attribute. - inputField: the ZK input object (ZK Framework). - inputFields: a map to get access to any other ZK input object (ZK Framework). - serviceLocator: locator to use any Soffid engine microservice. ##### Example 1 Into the attribute mappings save the value of account metadata: ``` varX <= accountAttributes{"att_name"} ``` ##### Example 2 Get the value from the attribute account metadata to use it into a trigger ```Java strValue = source.get("attributes").get("att_name"); if (strValue != null) { ..... ..... } else { ..... ..... } ``` ## Actions #### Agents query actions| **Query** | Allows you to query roles through different search systems, [Basic and Advanced](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/search-types "Search Types"). |
| **Add new** | Allows you to add a new agent to the system. You can choose that option on the hamburger menu or click the add button (+). To add a new role it will be mandatory to fill in the required fields |
| **Delete** | Allows you to remove one or more agents by selecting one or more records and next clicking the button with the subtraction symbol (-). To perform that action, Soffid will ask you for confirmation, you could confirm or cancel the operation. |
| **Download CSV file** | Allows you to download a CSV file with the basic information of all agents. |
| **Apply changes** | Allows you to create a new agent or update an existing agent. To save the data it will be mandatory to fill in the required fields |
| **Preview changes** | When there are some changes to be applied (when the configuration agent is updated), you can check them with this option. If you click this button, Soffid will display a new window with the list of users to be updated. |
| **Apply now** | When the configuration agent is updated, this button will be displayed. If you click this option the update action will be performed. The progress bar will be displayed during the execution of the process. This action is performed asynchronously. |
| **Delete** | Allows you to delete a specific agent. You can choose that option on the trash icon. To perform that action, Soffid will ask you for confirmation, you could confirm or cancel the operation. |
| **Undo** | Allows you to quit without applying any changes made. |
| **Import** | Allows you to upload an XML file with the attribute mapping data. This option deletes previous attribute mappings and creates new attribute mapping. |
| **Export** | Allows you to export an XML file with attribute mappings. |
| **Create default mapping** | Allows you to create automatically default mappings for the specific Type selected. |
| **Test** | Check if there is a connection to the target system. |
| **Open flow** | Opens a window with the workflow. |
| **Test** | Allows you to test the workflow. |
| **Apply changes/Save** | Allows you to update the agent with the changes made on Attribute mappings. |
| **Add System Objects** | Allows you to add a new system object based on a Soffid object. You need to click the button with the add symbol (+) located at the end of the row of System Objects. Once you click the button, Soffid adds new fields to the form to add new attributes, properties, and/or Triggers depending on the agent type. It is mandatory to apply changes by clicking the diskette button to update the agent. |
| **Delete System Objects** | Allows you to delete a system object. You need to click the button with the subtraction symbol (-) located at the end of the row system object which you want to delete. It is mandatory to apply changes by clicking the diskette button to update the agent. |
| **Add Property** | Allows you to add properties to a specific system object. You need to click the button with the add symbol (+) located at the end of the row of Properties. Once you click the button, Soffid adds new fields to the form to add the property. It is mandatory to apply changes by clicking the diskette button to update the agent. |
| **Delete Property** | Allows you to delete properties from a specific system object. You need to click the button with the subtraction symbol (-) located at the end of the row property which you want to delete. It is mandatory to apply changes by clicking the diskette button to update the agent. |
| **Add System attribute** | Allows you to add attribute mappings to a specific system object. You need to click the button with the add symbol (+) located at the end of the row of the System attribute. Once you click the button, Soffid adds new fields to the form to add the attribute. It is mandatory to apply changes by clicking the diskette button to update the agent. |
| **Detele System attribute** | Allows you to delete attribute mappings of a specific system object. You need to click the button with the subtraction symbol (-) located at the end of the row System attribute which you want to delete. It is mandatory to apply changes by clicking the diskette button to update the agent. |
| **Test expression** | Allows you to test a system object. When you click that option, Soffid will show you new fields and operations to test the system attribute config. |
| **Synchronize now** | Allows you to synchronize a specific system object to the target system. |
| **Fetch system raw data** | Brings the data of a specific system object from a target system. |
| **Fetch Soffid object** | Brings the data of a specific system object with processed data to update into Soffid |
| **Add Trigger** | Allows you to add a trigger to a specific system object that will be executed when data is loaded into a target system. You need to click the button with the add symbol (+) located at the end of the row of Trigger. Once you click the button, Soffid adds new fields to the form to add the trigger. It is mandatory to apply changes by clicking the diskette button to update the agent. |
| **Delete Trigger** | Allows you to delete a trigger of a specific system object. You need to click the button with the subtraction symbol (-) located at the end of the row Trigger which you want to delete. It is mandatory to apply changes by clicking the diskette button to update the agent. |
| **Apply changes** | Allows you to update the Load trigger data with the changes made on the Load Trigger |
| **Add Trigger** | Allows you to add a trigger that will be executed when data is loaded into Soffid. You need to click the button with the add symbol (+) located at the end of the row. Once you click the button, Soffid adds new fields to the form to add the trigger. Then you need to select the Object and the type of trigger and write the customized script. Finally, you need to apply changes to update the agent. |
| **Delete Trigger** | Allows you to delete a trigger. You need to click the button with the subtraction symbol (-) located at the end of the row which you want to delete. It is mandatory to apply changes by clicking the diskette button to update the agent. |
| **Provisioning all users on to managed systems** | Run the process to ensure the users are created, with proper permissions, updated, disabled, or deleted on to managed systems. |
| **Propagate groups to agent** | Run the process to push all the groups of Soffid into the managed system. |
| **Reconcile (load target system objects)** | Run the process to discover new, changed, deleted, or orphaned accounts to determine user access privileges. |
| **Load authoritative data for identities and groups** | Run the process to load data of groups and data of identities from the managed system into Soffid |
| **Generate target system potential impact** | Generate a report with all the potential changes that would be performed on the managed system. |
| **Add account metadata** | Allows you to update the agent with the changes made on metadata. |
| **Add account metadata** | Allows you to add account metadata. You need to click the button with the add symbol (+) located at the end of the row. Once you click the button, Soffid shows you an empty form to fill in with the new account metadata. Finally, you need to apply changes. |
| **Delete account metadata** | Allows you to delete one account metadata. First, you need to click on the account metadata which you want to delete. Then Soffid shows a form with the detailed account metadata. On the hamburger icon of that form, you can find the delete action. In this case, Soffid will not ask you for confirmation to delete. |
You could find a set of sample scripts: [Sample scripts](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/sample-scripts "Sample scripts")
You could find a link with the SCIM Query Language used in some methods as findUserByJsonQuery("query"). You can visit the [SCIM chapter](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/scim "SCIM").
Below you could find a set of custom utility classes: [Utility classes](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/utility-classes "Utility classes")
--- ## More information ### Password synchronization The passwords a user has on an agent will be synchronized with any other "single user account" the user has on this agent. Shared accounts will never get their password synchronized. Password in an agent will be also synchronized with any other account the user has on other agents that are sharing the same password domain. The password change can be produced by an operator using the Soffid console, the user itself using the Soffid Self Service portal, or a timed automatic task. Furthermore, some managed systems can forward their password to Soffid in order to get them synchronized. In order to accept these password changes coming from managed systems, the trusted passwords box must be checked for the source agent. Mind that this is the flow for normal user passwords. Temporary passwords generated by the Soffid console will only be sent to agents marked as trusted. Agents not checked as trusted will have a random new password instead. Later, when the user changes the password on Soffid or any trusted system, the new password will be notified to Soffid by the managed system, and every agent on the same password domain will actually get the new password. ### Agents account management The agent configuration sets the way accounts are created and disabled. Whenever a user is modified, the following rules will be applied to check if the user should have or not an account on this agent: 1. The user type is checked against valid user types. 2. If there is a business unit or group bound to the agent, the user membership will be assessed. 3. If the role based box is checked, the system will verify if the user has any role or entitlement assigned to this agent. If the user does not apply for any of the conditions, every account the user has at this agent will be changed to Disabled status. If the user verifies every one of the conditions, the user can have an account on this agent. Every account the user has at this agent will be changed to Enabled status. Unless the "Manual account creation" is checked, if the user can have an account on this agent, but it has no one, the account creation method will be invoked. To create it, Soffid will search for the user domain bound to this agent and will follow its configuration. If the user domain is configured with a script, this script will be executed and the result value will be accepted as the new account name. Mind that if the script returns a null value, no account can be created. If the returning value from the script clashes with an existing account, the existing account will remain unchanged, unless the existing account is marked as an unmanaged account. In such a case, the account will be changed from an unmanaged state to a single user. --- ## Operational ### Monitoring After the agent configuration you could check on the monitoring page if the service is running in the Synchronization Server, please go to: `Main Menu > Administration > Monitoring and reporting > Syscserver monitoring` ### Tasks #### Authoritative If you are checked "Authorized identity source", an automatic task to load identities from the managed system to Soffid is available, please go to: `Main Menu > Administration > Monitoring and reporting > Scheduled tasks` And you will something like "Import authoritative data from <AGENT\_NAME>". [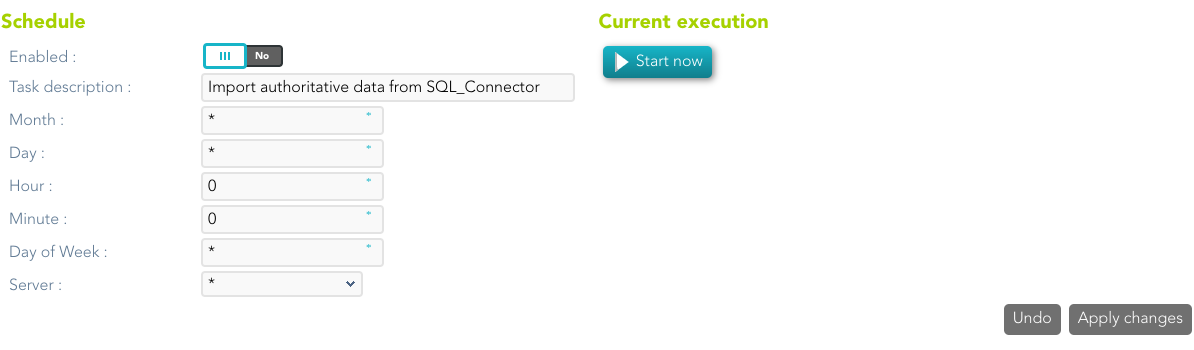](https://bookstack.soffid.com/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/image-1659012997074.png) You can also run the Authoritative load from the Massive actions tab in the Agent [](https://bookstack.soffid.com/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/image-1659013094703.png) #### Reconcile If you are configured the "Attribute Mapping" tab with some of our objects: "user, account, role, group or grant", an automatic task to synchronize these objects from the managed system to Soffid is available, please go to: `Main Menu > Administration > Monitoring and reporting > Scheduled tasks` And you will do something like "Reconcile all accounts from <AGENT\_NAME>". [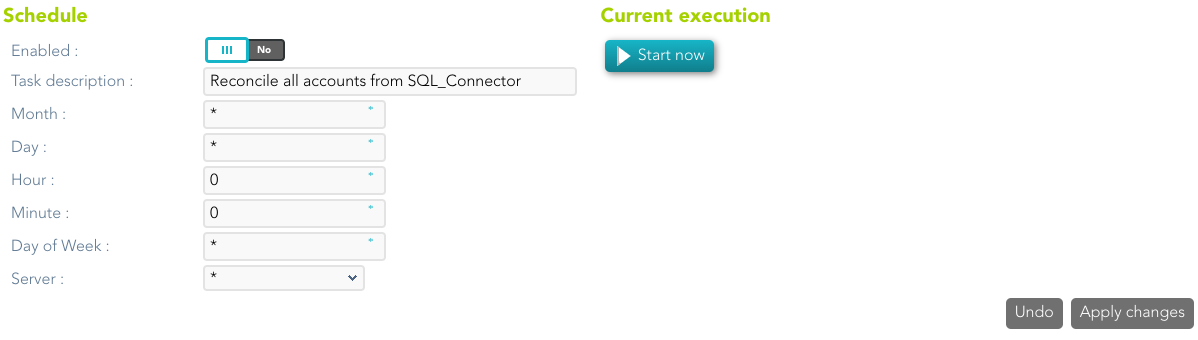](https://bookstack.soffid.com/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/image-1659013025873.png) You can also run the Reconcile from the Massive actions tab in the Agent [](https://bookstack.soffid.com/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/image-1659013126808.png) ### Synchronization Regarding the synchronization of the objects, there are two possible options: - If the "Read Only" attribute is checked in the "Basics" tab (select Yes option), only the changes in the managed systems will be updated in Soffid. We recommend these options until the global configuration of Soffid will be tested. - If the "Read Only" attribute is not checked in the "Basics" tab (select No option), all the changes in Soffid or the managed system will be updated in the other. Note that this synchronization must be configured in the "Basic" tab correctly. --- # Synchronization servers ## Description Sync server is the engine responsible for connecting Soffid with data sources or managed systems. Soffid allows you to configure different synchronization servers. These synchronization servers are **installed and configurated using command line tool.**More information about how to install sync server on [the Installation chapter](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/installation). Here you can find information on how to install a sync server in different environments.
Whenever an action is performed on any Soffid object, a synchronization task is created in Soffid database. Initially, most of the tasks should be forwarded to every managed system connector. The specific system connector will be responsible for applying (or ignoring) the task to the managed system. The normal synchronization server flow for a task is as follows: 1. Engine timely reads pending tasks table (SC\_TASQUE). To avoid two sync servers to process the same task, the column TAS\_SERVER is updated to reflect the actual server that is processing it. **2. **Engine manage tasks priorities and updates the task queue. Engine keeps track of one task queue for each managed system connector. Soffid allows you to configure the parameter **soffid.sync.engine.threads** with the number of threads available to run the tasks.For more information about this parameter you can visit [the Soffid Parameter page](https://bookstack.soffid.com/link/86#bkmrk-parameter-descriptio-0).
3. Engine has created some execution threads to forward each task to the specific connector class. During this process, dispatcher can decide to reject (mark as done) the task without forwarding it. **4. **The specific connector class gets additional information about the task from core services. 5. Task is removed from database when every dispatcher has done it. This architecture and its optimized engine allow Soffid to achieve great performance. ## Screen overview [](https://bookstack.soffid.com/uploads/images/gallery/2022-01/image-1641823484543.png) [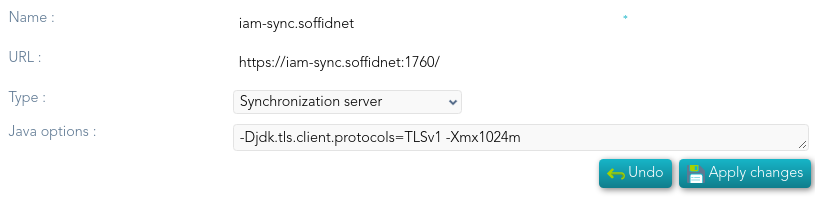](https://bookstack.soffid.com/uploads/images/gallery/2022-01/image-1641823523641.png) ## Standard attributes - **Name**: name of the synchronization server. - **URL**: URL of the synchronization server. - **Type**: there are different kinds of synchronization servers: - **Synchronization server**: that server connects to the main database and allocates the task to the different agents. - **Synchronization agent proxy**: uses a push mechanism. The main Synchronization server will send the tasks to the synchronization agent proxy when it detects tasks for the proxy. That server does not connect to the main database. - **Remote synchronization server**: uses a pull mechanism. That server is asking for its tasks, when it asks and the Synchronization server has a task for the remote, the Synchronization server will send that tasks. That server does not connect to the main database. - **Synchronization agent gateway**: this server is the broker between the main synchronization server and the remote servers. - **Java options**: additional parameters to pass to JVM (Java Virtual Machine). Some useful parameters: - For a high capacity server are: `-Xmx1024M` - For debugging communication: -Djavax.net.debug=ssl - To enable sync server to use old TLS version in client connections (from sync server to a managed system) add `-Djdk.tls.client.protocols=TLSv1,TLSv1.1` (Be in mind TLSv1.2 will be the default version, but some old applications can use TLSv1) - To enable sync server to use old TLS version for incoming connections (from a server or desktop to the sync server) add `-Dsoffid.tls.protocols=TLSv1.1,TLSv1,TLSv1.2,TLSv1.3 -Dsoffid.tls.excludedCiphers="^.*_(MD5)$" `Mind that the system security can be compromised by using deprecated TLS protocols - To define how long Java keeps the DNS (domain name resolution) responses in cache you can add the paramameters `-Dsun.net.inetaddr.ttl=1` or the newest `-Dsun.net.inetaddr.ttl=1 ` "time-to-live" (TTL).If you change the Java Options of an existing Syncserver, you will need to restart the Syncserver. You can visit the [Sync server monitoring](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/sync-server-monitoring "Sync server monitoring") page for more information about how to restat the Syncserver.
If you are working on Soffid Console version 2.x to change the capacity you need to edit the iam-console.vmoptions file and change the -Xmx attribute.
## Actions #### Synchronization server query| **Download CSV file** | Allows you to download a CSV file with the information of all synchronization servers. |
| **Apply changes** | Allows you to save the synchronization server data and quit. |
| **Save** | Allows you to save the synchronization server data |
| **Undo** | Allows you to undo the changes to quit without save them. |
| **Delete** | To delete a sync server you can click on the hamburger icon and then click the delete button (trash icon). Soffid will ask you for confirmation to perform that action, you could confirm or cancel the operation. |
Account naming rules define how to generate account names to connect with final systems. The normal case is the account name will be the same as the user name, in other cases, here you could define the customized account name rules.
When you are configuring an agent, you have to indicate the user domain which will be used to create new accounts, that user domain refers to the Account naming rules defined on the Soffid console. You can visit the [Agents](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/agents "Agents") page for more information. ## Standard attributes - **Code**: code used to identify the account naming rule. - **Description**: a brief description of the rule. That value will be displayed to select the user domain on the agent's setup. - **User domain type**: use to define the kind of - Main user name: use the main user name. - Assigned by the operator: the operator will assign the account name. - Script: allows you to configure the script condition and script creation of account naming. - Server Addon: allows selecting an addon to generate the account naming rules. - **Generator**: allows you to select an addon when the user domain type selected is "Server addon". - **Create account condition**: defines the conditions to enable or prevent the creation of the account. It is only available when the Script option is selected in the User domain type. - **Script**: computes the name to assign to the user account. If the script returns null, the account is not going to be created. It is only available when the Script option is selected in the User domain type. --- #### Create account condition The create account condition enables or prevents the creation of the account. ##### Available objects| user | User object: [Details](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/latest/uml/com/soffid/iam/api/User.html) |
| attributes | User attributes map |
| groups | The groups that the user belongs to. It's composed of a java map. The key is the group name, and the value is the [Group object](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/latest/uml/com/soffid/iam/api/Group.html) |
| groupsList | The groups that the user belongs to. It's composed of a java list of [Group objects](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/latest/uml/com/soffid/iam/api/Group.html) |
| serviceLocator | [Helper](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/latest/iam-core/apidocs/com/soffid/iam/ServiceLocator.html) to get access to Soffid microservices |
| userDomain | [User domain](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/2.8.1/uml/com/soffid/iam/api/UserDomain.html) object |
| system | [Target system](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/2.8.1/uml/com/soffid/iam/api/Application.html) object |
| boolean | Return true if the account can be created |
| user | User object: [Details](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/latest/uml/com/soffid/iam/api/User.html) |
| attributes | User attributes map |
| groups | The groups that the user belongs to. It's composed of a java map. The key is the group name, and the value is the [Group object](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/latest/uml/com/soffid/iam/api/Group.html) |
| groupsList | The groups that the user belongs to. It's composed of a java list of [Group objects](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/latest/uml/com/soffid/iam/api/Group.html) |
| serviceLocator | [Helper](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/latest/iam-core/apidocs/com/soffid/iam/ServiceLocator.html) to get access to Soffid microservices |
| userDomain | [User domain](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/2.8.1/uml/com/soffid/iam/api/UserDomain.html) object |
| system | [Target system](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/2.8.1/uml/com/soffid/iam/api/Application.html) object |
| String | Return the account name to use |
| **Add new** | Allows you to add a new account naming rule in the system. To add a new agent it is necessary to fill in the required fields. |
| **Delete** | Allows you to remove one or more agents by selecting one or more records on the list. |
| **Export** | Allows you to export a CSV file with the account naming rules configuration. |
| **Import** | Allows you to upload a CSV file with the account naming rules configuration to add new rules to the system. First, you need to pick up a CSV file, that CSV has to contain a specific configuration. Then you need to check the contents. And finally, you need to select the mappings for each column of the CSV file to import the data correctly and click the Import button. |
| **Apply changes** | Allows you to save new account naming rules or to save an updated account naming rule. |
| **Undo** | Allows you to undo any changes made. |
| **Delete** | Allows you to remove one account naming rule. |
| **Query** | Allows to query groups through different search systems, [Quick, Basic and Advanced](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/search-types "Search Types"). |
| **Add new** | Allows you to add a new attribute translation table. That option adds a new row on the table to fill in the data. It will be mandatory to apply changes to save the data. |
| **Delete** | Allows you to remove one or more agents by selecting one or more records on the list. Or delete one by one. |
| **Import** | Allows you to upload a CSV file with the attribute translation table data to add to the system. First, you need to pick up a CSV file, that CSV has to contain a specific configuration. Then you need to check the contents. And finally, you need to select the mappings for each column of the CSV file to import the data correctly and to click the Import button. |
| **Download CSV file** | Allows you to download a CSV file with the information of all attribute translation tables. |
| **Apply changes** | Allows you to save new attribute translation tables or to save updated attribute translation tables. |
| **Undo** | Allows you to undo any changes made. |
**Attribute** | **Type** | **Description** |
|---|---|---|
| id | Long | user id |
| accountId | Long | account id |
| accountName | String | account name |
| system | String | managed system (agent) name |
| accountDescription | String | account description |
| active | Boolean | true if user is active |
| accountDisabled | Boolean | true if account is diabled |
| mailAlias | String | blank separated mails |
| userName | String | user name |
| primaryGroup | String | user's primary group name |
| comments | String | user's comments |
| createdOn | Date | user creation date |
| modifiedOn | Date | user last modification date |
| mailDomain | Date | user mail domain ( email right side of @) |
| fullName | String | user full name |
| shortName | String | user mail name (email left side of @) |
| firstName | String | user first name |
| lastName | String | user last name |
| lastName2 | String | user second last name (when applicable) |
| mailServer | String | mail server host name |
| homeServer | String | home drive server host name |
| profileServer | String | roaming profile server host name |
| phone | String | user's phone number |
| userType | String | user type |
| createdBy | String | user name creator of this user |
| modifiedBy | String | user name modifier of this user |
| secondaryGroups | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [groups](#bkmrk-group-object) the user belongs to, including primary group The attributes of the inner map are described later |
| attributes | Map<String,String> | additional user attributes |
| grantedRoles | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [grants](#bkmrk-grant-object) directly granted to the user |
| allGrantedRoles | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [grants](#bkmrk-grant-object) directly on indirectly granted to the user |
| granted | List<String> | list of role names and group names directly granted to the user |
| allGranted | List<String> | list of role names and group names directly or indirectly granted to the user |
**Attribute** | **Type** | **Description** |
|---|---|---|
| accountDescription | String | account description |
| accountDisabled | Boolean | true if account is diabled |
| accountId | Long | account id |
| accountName | String | account name |
| allGranted | List<String> | list of role names directly or indirectly granted to the user |
| allGrantedRoles | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [grants](#bkmrk-grant-object) directly on indirectly granted to the user |
| attributes | Map<String,String> | additional account attributes |
| granted | List<String> | list of role names directly granted to the user |
| grantedRoles | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [grants](#bkmrk-grant-object) directly granted to the user |
| lastLogin | Calendar | lastLogin |
| lastPasswordUpdate | Calendar | lastPasswordUpdate |
| lastUpdate | Calendar | lastUpdate |
| passwordExpiration | Calendar | passwordExpiration |
| passwordPolicy | String | password policy |
| system | String | managed system (agent) name |
| type | AccountType | "U"=user, "S"=shared, "P"=privileged, "I"=ignored |
**Attribute** | **Type** | **Description** |
|---|---|---|
| groupId | Long | group id |
| name | String | group name |
| description | String | group description |
| parent | String | parent group name |
| server | String | home server host name |
| disabled | boolean | true if the group is disabled |
| accountingGroup | String | group accounting information |
| type | String | group type |
| driveLetter | String | home server letter to connect to |
| users | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [users](#bkmrk-user-object) belonging to this group |
| userNames | List<String> | list of user names belonging to this group |
| allUsers | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [users](#bkmrk-user-object) directly or indirectly belonging to this group |
| allUserNames | List<String> | list of user names either directly or indirectly grantee of this role |
| grantedRoles | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [roles](#bkmrk-role-object) granted to this group |
| grantedRoleNames | List<String> | list of role names granted to this group |
**Attribute** | **Type** | **Description** |
|---|---|---|
| roleId | Long | role id |
| system | String | managed system (agent) name |
| name | String | role name |
| application | String | application system name |
| category | String | role category |
| passwordProtected | boolean | true if role should be password protected (where applicable) |
| description | String | Role description |
| wfmanaged | boolean | true if role should be displayed in self service requests |
| domain | String | custom domain for this role: Use com.soffid.iam.api.DomainType constants or configured custom domain |
| ownedRoles | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of[ roles granted](#bkmrk-grant-object) to this one |
| ownerRoles | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [roles grantee](#bkmrk-grant-object) of this one |
| ownerGroups | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [groups](#bkmrk-group-object) grantee of this role |
| grantedAccountNames | List<String> | list of account names directly grantee of this role |
| grantedAccounts | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [users](#bkmrk-user-object) directly grantee of this role |
| allGrantedAccountNames | List<String> | list of account names either directly or indirectly grantee of this role |
| allGrantedAccounts | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [users](#bkmrk-user-object) either directly or indirectly grantee of this role |
| attributes | Map<String,Object> | role's custom attributes |
**Attribute** | **Type** | **Description** |
|---|---|---|
| domainValue | String | grant value (if any) |
| grantedRole | String | granted role name |
| grantedRoleId | Long | granted role id |
| grantedRoleObject | [role object](#bkmrk-role-object) | granted role |
| grantedRoleSystem | String | granted role managed system (agent) name |
| id | Long | grant id |
| ownerAccount | String | grantee account name |
| ownerAccountObject | [account object](#bkmrk-account-object) | grantee account |
| ownerGroup | String | grantee group name |
| ownerRoleId | String | grantee role id |
| ownerRoleName | String | grantee role name |
| ownerSystem | String | grantee account or role managed system name |
| ownerUser | String | grantee user name |
By default, use the **grantedRole** object
The **grant** object adds the roles and the groups, use it only in this case
#### Examples ##### Grant Example to map a grant object (assign a role to an account):**System attribute** | **Direction** | **Soffid attribute** |
|---|---|---|
| role\_name | => | grantedRole |
| account\_name | => | ownerAccount |
**System attribute** | **Direction** | **Soffid attribute** |
|---|---|---|
| role\_name | => | grantedRole |
| parent\_role\_name | => | ownerRoleName |
**System attribute** | **Direction** | **Soffid attribute** |
|---|---|---|
| role\_name | => | grantedRole |
| parent\_role\_name | => | ownerRoleName |
| group\_code | => | domainValue |
| group\_code | => | holderGroup |
| userName | => | ownerUser |
**Attribute** | **Type** | **Description** |
|---|---|---|
| id | Long | internal mail list id |
| name | String | mail list name ( the initial part, before the @ sign) |
| domain | String | mail list domain ( the remaining part after the @ sign) |
| system | String | managed system (agent) name |
| description | String | mail list description |
| users | String array | user names that are bound to this mail list |
| groups | String array | group names thta are subscribed to this mai list |
| roles | String array | role names that grant access to this mail list |
| lists | String array | Nested mail lists |
| explodedUsers | String array | Names of the users that should be subscribed to this mail list, including the users that should be subscribed due to group or role membership |
| explodedUserAddresses | String array | Mail addresses of any exploded User |
**Attribute** | **Type** | **Description** |
|---|---|---|
| userName | String | User name |
| user | Map<String,Object> | [user object](#bkmrk-user-object) |
| groupName | String | Group name |
| group | Map<String,Object> | [group object](#bkmrk-group-object) |
| attributes | Map<String,Object> | Membership custom attributes |
**method name** | **parameters** | **result type** | **comments** |
|---|---|---|---|
| soffidToSystem | [ExtensibleObject](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/2.0.0-2/iam-common/apidocs/com/soffid/iam/sync/intf/ExtensibleObject.html) soffidObject | [ExtensibleObject](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/2.0.0-2/iam-common/apidocs/com/soffid/iam/sync/intf/ExtensibleObject.html) | Uses attribute translation tables to transform a soffid object to a target system object. Mind to fill-in objectType property to use the proper object mapping |
| systemToSoffid | [ExtensibleObject](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/2.0.0-2/iam-common/apidocs/com/soffid/iam/sync/intf/ExtensibleObject.html) systemObject | [ExtensibleObject](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/2.0.0-2/iam-common/apidocs/com/soffid/iam/sync/intf/ExtensibleObject.html) | Uses attribute translation tables to transform a target system object to a Soffid object. Mind to fill-in objectType property to use the proper object mapping |
| search | [ExtensibleObject](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/2.0.0-2/iam-common/apidocs/com/soffid/iam/sync/intf/ExtensibleObject.html) exampleObject | [ExtensibleObject](http://www.soffid.org/doc/console/2.0.0-2/iam-common/apidocs/com/soffid/iam/sync/intf/ExtensibleObject.html) | Uses the exampleObject to perform a query by example on the target system. If the object exists on the target system, it is returned. Mind to fill-in objectType property with the desired system object type |
| invoke | String verb String action Map parameters | List of Map | This method allows arbitrary executions on the target system, but it semantics can change depending on the connector used. For instance, it can be used to perform a GET on the target system in REST connector, can issue an LDAP query on ActiveDirectory connector, can execute a SELECT sentence on a SQL connector, or can execute an operating system command in Shell connector. The results are returned as a list of objects (map). |
**Attribute** | **Type** | **Description** |
|---|---|---|
| id | Long | user id |
| accountId | Long | account id |
| accountName | String | account name |
| system | String | managed system (agent) name |
| accountDescription | String | account description |
| active | Boolean | true if user is active |
| accountDisabled | Boolean | true if account is diabled |
| mailAlias | String | blank separated mails |
| userName | String | user name |
| primaryGroup | String | user's primary group name |
| comments | String | user's comments |
| createdOn | Date | user creation date |
| modifiedOn | Date | user last modification date |
| mailDomain | Date | user mail domain ( email right side of @) |
| fullName | String | user full name |
| shortName | String | user mail name (email left side of @) |
| firstName | String | user first name |
| lastName | String | user last name |
| lastName2 | String | user second last name (when applicable) |
| mailServer | String | mail server host name |
| homeServer | String | home drive server host name |
| profileServer | String | roaming profile server host name |
| phone | String | user's phone number |
| userType | String | user type |
| createdBy | String | user name creator of this user |
| modifiedBy | String | user name modifier of this user |
| secondaryGroups | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [groups](https://confluence.soffid.com/display/SOF/group+object) the user belongs to, including primary group The attributes of the inner map are described in the link |
| secondariGroups2 | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of user [memberships](https://confluence.soffid.com/display/SOF/membership+object), excluding primary group The attributes of the inner map are described link |
| attributes | Map<String,String> | additional user attributes |
| grantedRoles | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [grants](https://confluence.soffid.com/display/SOF/grant+object) directly granted to the user |
| allGrantedRoles | List<Map<String,Object>> | list of [grants](https://confluence.soffid.com/display/SOF/grant+object) directly on indirectly granted to the user |
| granted | List<String> | list of role names and group names directly granted to the user |
| allGranted | List<String> | list of role names and group names directly or indirectly granted to the user |
Note that Soffid supports different scripting languages, you can configure it in the[ Smart engine settings screen](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/smart-engine-settings).
Additionally, in the initial configuration of the container, we can configure the SOFFID\_TRUSTED\_SCRIPTS environment variable to allow the use of insecure classes. You can find this information visiting [the Installing IAM Console page](https://bookstack.soffid.com/link/27#bkmrk-4.-installation).
## Table of contents 1. [Agent scripts](#bkmrk-agent-scripts) - [User full name](#bkmrk-user-full-name) - [Create mainDomain if it doesn't exit](#bkmrk-create-maindomain-if) - [Recover active agents](#bkmrk-recover-active-agent) - [Show by a user the agents that have associates](#bkmrk-show-by-a-user-the-a) 2. [Identity scripts](#bkmrk-identity-scripts) - [Recover a user for userName](#bkmrk-recover-a-user-for-u) - [Recover a users from a Jquery](#bkmrk-recover-a-users-from) - [Print some attributes](#bkmrk-print-some-attribute) - [Print by user the email](#bkmrk-print-by-user-the-em) - [Print by user some additional data](#bkmrk-print-by-user-some-a) - [Create a new identity](#bkmrk-create-a-new-identit) - [Update an identity](#bkmrk-update-an-identity) - [Delete an identity](#bkmrk-delete-an-identity) 3. [Account scripts](#bkmrk-account-scripts) - [Recover accounts of user](#bkmrk-recover-accounts-of-) - [Remove attribute values of a metadata](#bkmrk-remove-attribute-val) 4. [Role scripts](#bkmrk-role-scripts) - [Recover roles of a user](#bkmrk-recover-roles-of-a-u) - [Print the associated roles for each account](#bkmrk-print-the-associated) - [Print for an account the roles and applications for each of them](#bkmrk-print-for-an-account) - [Print the roles associated with each account](#bkmrk-print-the-roles-asso) - [Create a new role](#bkmrk-create-a-new-role) - [Update a role](#bkmrk-update-a-role) - [Delete a role](#bkmrk-delete-a-role) - [List the roles of an application](#bkmrk-list-the-roles-of-an) 5. [Mail scripts](#bkmrk-5.-mail-scripts) - [Send email](#bkmrk-send-email) --- ## 1. Agent scripts #### User full name ```Java return firstName + lastName; ``` #### Create mainDomain if it doesn't exit ```Java String mailDomain = null; if (email != void && email != null && email.contains("@")) { String[] mailTokens = email.split("@"); mailDomain = mailTokens[1]; } com.soffid.iam.service.MailListsService service = com.soffid.iam.ServiceLocator.instance().getMailListsService(); com.soffid.iam.api.MailDomain domain = service.findMailDomainByName(mailDomain); if (domain==null) { domain = new com.soffid.iam.api.MailDomain(); domain.setCode(mailDomain); domain.setDescription(mailDomain); domain.setObsolete(new Boolean(false)); domain = service.create(domain); } return mailDomain; ``` #### Recover active agents ```Java llistaAgents = serviceLocator.getDispatcherService().findAllActiveDispatchers(); for(agent:llistaAgents) { out.println("Nom: " + agent.name); out.println("Class Name: " + agent.className + "\n"); } ``` #### Show by a user the agents that have associates ```Java llistaUsuaris = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserByJsonQuery("userName eq \"Ivan\" "); for(usuari:llistaUsuaris) { out.println("Usuario: " + usuari.userName); llisstacuentas = serviceLocator.getAccountService().findAccountByJsonQuery("users.user.userName eq \""+usuari.userName+"\" "); for(cuenta:llisstacuentas){ out.print(" Cuenta : " + cuenta.name); out.println(" ID: " + cuenta.id); llistaRole = serviceLocator.getApplicationService().findRoleAccountByAccount(cuenta.id); for(role:llistaRole){ out.print(" Role: " + role.roleName + "\n"); out.println(" Aplicacion: " + role.informationSystemName); out.println(" Agente: " + role.system); } } } ``` --- ## 2. Identity scripts #### Recover a user for userName ```Java u = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserByUserName("Ivan"); out.print("Usuari: " + u.firstName); ``` #### Recover a users from a Jquery ```Java llistaUsuari = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserByJsonQuery("firstName sw \"A\" AND lastName sw \"V\" "); for (usuari:llistaUsuari){ out.println("Usuari: " + usuari.userName); } ``` #### Print some attributes ```Java u = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserByUserName("02"); out.println("UserName: " + u.userName); out.println("Name: " + u.firstName); out.println("LastName: " + u.lastName); ``` #### Print by user the email ```Java u = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserByUserName("02"); out.print("Email: " + u.shortName + "@" + u.mailDomain); ``` #### Print by user some additional data ```Java llistaDadesUsuari = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserDataByUserName("18008366X"); for(dadaUsuari:llistaDadesUsuari){ out.println("Atributs " + dadaUsuari.attribute + " = " + dadaUsuari.value); } ``` #### Create a new identity ```Java try { newUser = new com.soffid.iam.api.User(); //Instanciar un nuevo objeto de tipo usuario newUser.userName = "IvanVis"; //Faltan 6 parametres newUser.firstName = "Ivannn"; newUser.lastName = "Visarttt"; newUser.userType = "I"; newUser.profileServer = "null" ; newUser.homeServer = "null" ; newUser.mailServer = "null" ; newUser.primaryGroup = "world"; newUser.active = true; serviceLocator.getUserService().create(newUser); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(out); } ``` #### Update an identity ```Java u = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserByUserName("Ivan"); u.firstName = "Ivaaan1"; u = serviceLocator.getUserService().update(u); out.print(u.firstName); out.print(u.userName); ``` #### Delete an identity ```Java try { u = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserByUserName("02"); serviceLocator.getUserService().delete(u); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(out); } ``` --- ## 3. Account scripts #### Recover accounts of user ```Java la = serviceLocator.getAccountService().findAccountByJsonQuery("users.user.userName eq \"02\" "); for(a:la) { out.println("Cuenta: " + a.name); out.println("ID: " + a.id); out.println("System: " + a.system + "\n"); } ``` #### Remove attribute values of a metadata ```Java public void removeUnAttributeValues(String attribute, String system) { la = serviceLocator.getAccountService().findAccountByJsonQuery("system eq \""+system+"\""); for (a : la) { laa = serviceLocator.getAccountService().getAccountAttributes(a); for (aa : laa) { if (aa.attribute.equals(attribute)) { if (aa.value!=null) { out.print("accountName: "+accountName+", attribute.value: "+aa.value); serviceLocator.getAccountService().removeAccountAttribute(aa); out.println(" ---> removed"); } } } } } removeUnAttributeValues("manager","OSCM"); ``` --- ## 4. Role scripts #### Recover roles of a user ```Java user = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserByUserName("Ivan"); out.println("Usuari: " + user.userName + "\n"); rolsUser = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserRolesHierachyByUserName(user.userName); for(listrRolsUser:rolsUser){ out.println("Nombre: " + listrRolsUser.name); out.println("Descripcion: " + listrRolsUser.description); out.println(); } ``` #### Print the associated roles for each account ```Java llistaUsuaris = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserByJsonQuery("userName eq \"Ivan\" "); for(usuari:llistaUsuaris){ llisstacuentas = serviceLocator.getAccountService().findAccountByJsonQuery("users.user.userName eq \""+usuari.userName+"\" "); for(cuenta:llisstacuentas){ out.print(" Cuenta : " + cuenta.name); llistaRole = serviceLocator.getApplicationService().findRoleAccountByAccount(cuenta.id); for(role:llistaRole){ out.print(" Role: " + role.roleName + "\n"); } } } ``` #### Print for an account the roles and applications for each of them ```Java llistaUsuaris = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserByJsonQuery("userName eq \"Ivan\" "); for(usuari:llistaUsuaris){ llisstacuentas = serviceLocator.getAccountService().findAccountByJsonQuery("users.user.userName eq \""+usuari.userName+"\" "); for(cuenta:llisstacuentas){ out.print(" Cuenta : " + cuenta.name); out.println(" ID: " + cuenta.id); llistaRole = serviceLocator.getApplicationService().findRoleAccountByAccount(cuenta.id); for(role:llistaRole){ out.print(" Role: " + role.roleName + "\n"); out.println(" Aplicacion: " + role.informationSystemName); } } } ``` #### Print the roles associated with each account ```Java usuCuenta = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserByJsonQuery(""); for(listaUsuCuenta:usuCuenta) { out.println("Usuario: " + listaUsuCuenta.userName); out.println("Nombre: " + listaUsuCuenta.firstName); rolsUser = serviceLocator.getUserService().findUserRolesHierachyByUserName(listaUsuCuenta.userName); for(listaRolsUser:rolsUser){ out.println("Nombre del Rol: " + listaRolsUser.name); out.println("Descripcion: " + listaRolsUser.description); out.println(); } } ``` #### Create a new role ```Java try { newRol = new com.soffid.iam.api.Role(); newRol.name = "Rol_New_Script"; newRol.description = "Rol Script"; newRol.informationSystemName = "SOFFID"; newRol.system = "APLICACION01"; serviceLocator.getApplicationService().create(newRol); } catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(out); } ``` #### Update a role ```Java editRole = serviceLocator.getApplicationService().findRoleByJsonQuery("name eq \"Rol editado por script\" and informationSystemName eq \"APLICACION01\" "); for (role:editRole){ out.println(role.name); role.name = "ROL01"; role = serviceLocator.getApplicationService().update(role); out.print(role.name); } ``` #### Delete a role ```Java try { editRole = serviceLocator.getApplicationService().findRoleById(232734); serviceLocator.getApplicationService().delete(editRole); } catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(out); } ``` #### List the roles of an application ```Java list = serviceLocator.getApplicationService().findRoleByJsonQuery("informationSystemName eq \"SOFFID\""); for (role : list) { out.println(role.name); } ``` --- ## 5. Mail scripts #### Send email ```JavaScript import javax.mail.BodyPart; import javax.mail.internet.MimeBodyPart; import javax.activation.DataHandler; import javax.activation.FileDataSource; import java.util.ArrayList; path = "/tmp/"; name = "file.txt"; BodyPart att = new MimeBodyPart(); att.setDataHandler(new DataHandler(new FileDataSource(path+name))); att.setFileName(name); to = "aretha@soffid.com"; cc = "etaylor@soffid.com"; subject = "This is an email with attachment "; body = "In this email you can see an attachment."; mimeBodyParts = new ArrayList(); mimeBodyParts.add(att); serviceLocator.getMailService().sendHtmlMail(to, subject, body, mimeBodyParts); serviceLocator.getMailService().sendHtmlMail(to, cc, subject, body, mimeBodyParts); serviceLocator.getMailService().sendTextMailToActors(new String[]{"aretha"}, subject, body, mimeBodyParts); serviceLocator.getMailService().sendTextMailToActors(new String[]{"aretha"}, cc, subject, body, mimeBodyParts); out.println("Mails sent!"); ``` # Utility classes ## Crypt Crypt allows to encrypt text with different algorithms and verify the resulting hash. To use this class: `com.soffid.iam.crypt.Crypt` All methods are static: ```Java hash(String algorithm, String text) -> String pBKDF2Sha256(String text, String utf8Salt, int iterations) -> String pBKDF2Sha256(String text, byte []salt, int iterations) -> String pBKDF2Sha1(String text, String utf8Salt, int iterations) -> String pBKDF2Sha1(String text, byte []salt, int iterations) -> String genSaltBytes() -> byte[] // 8 bytes genSaltBytes(int size) -> byte[] genSalt() -> String // 8 bytes genSalt(int size) -> String verify(String algorithm, String text, String hash) -> boolean ``` The algorithms allowed are: - bcrypt - pBKDF2Sha256 - pBKDF2Sha1 (or pBKDF2) - Base64 (used by default is the algorithm is not in the previous list) One example: ```Java String myText = "abcd"; String myAlgorithm = "bcrypt"; String myHash = com.soffid.iam.crypt.Crypt.hash(myAlgorithm, myText); boolean isVerified = com.soffid.iam.crypt.Crypt.verify(myAlgorithm, myText, myHash); if (isVerified) { return myHash; } else { return null; } ``` ## CalendarConverter CalendarConverter allows to covert Calendar into String. To use this class: `com.soffid.iam.json.CalendarConverter` The methods (non static): ```Java toString(Calendar instance) -> String fromString(final String text) -> Calendar ``` One example: ```Java out.println(new com.soffid.iam.json.CalendarConverter().toString(date)); ``` # Network discovery {{@340}}