For more information to check if your system may be synchronized with this connector you do not hesitate to contact us through our [Contact form](http://www.soffid.com/contactform/)
### Prerequisites To enable LDAPS in your Active Directory, please read the following guide: [SSL access to Active Directory](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors/page/howto-ssl-access-to-active-directory "HOWTO SSL access to Active Directory"). It is needed an Active Directory user with full administrator access. ## Download and Install This addon is located in the Connectors section and its name is **Windows (including Active Directory)**.For more information about the installation process you can visit the [Addons Getting started](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/addons-getting-started/page/getting-started "Addons installation") page.
## Agent Configuration ### Basic #### Generic parameters After the installation of the addon, you may create and configure agent instances. This addon has 5 available agents: - Active Directory - Active Directory Only Passwords - Simple Windows AgentFor more information about how you may configure the generic parameters of the agent, see the following link: [Agents configuration](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/agents "Agents")
#### Custom parameters Below there are the specific parameters for this agent implementation, "Active Directory" - Host name of the domain controller. - Active Directory distingished name in X500 format. e.g.: dc=soffid,dc=local - Administrator principal name in X500 format, relative to A.D name. e.g.: cn=Administrator,cn=Users - Administrator password| **Parameter** | **Description** |
|---|---|
| Hostname | Host name of the server |
| LDAP base DN | LDAP Base name |
| Principal name | User name in DN format, including base name if needed |
| Password | Password for the user to connect. |
| Enable debug | Two options: \[ Yes / No \]. When it is enabled more log traces are printed in the Synchronization Server log |
| Accepted certificates | Two options: \[ Only trusted certificates / Any (insecure) \] |
| Follow referrals | Two options: \[ Don't / Yes \] If you select the Yes option, Soffid could follow the references to other systems if Soffid has the proper permissions. |
| Manage child domains | Two options: \[ No / Yes \] If you select the Yes option, Soffid will manage the domain referrals. |
| Create OUs when needed | Two options: \[ No / Yes \] If you select the Yes option and the OUs do not exist, these OUs will be created in the Active Directory. |
| Real time load last login attribute | Two options: \[ No / Yes \] |
| Real time load identity changes | Two options: \[ No / Yes \] You can check this option to synchronize the identities when Soffid is the authoritative data source. You must enable periodic synchronization. |
| **Property** | **Description** |
|---|---|
| rename | AD agent will always map account and group names to the SAMAccount attribute. BaseDN and cn can be calculated based on user attributes. AD agent is able to move and rename AD objects. If you don't desire users or groups to be renamed or moved, an object property named "**rename**" with the value "**false**" can be added to some object mappings. |
| searchBase | You can configure it if you want the reconciliation process to search accounts on a directory subtree other than AD root, put a searchBase property with the relative tree to look for. |
| key | The AD attribute works as the primary key. Usually, it's the sAMAccountName and can be omitted. |
| createDisabledAccounts | Set to true if you want the connector to create disabled accounts in the active directory. By default, disabled accounts are not created until enabled. |
| **System attribute** | **Description** |
|---|---|
| objectClass | Active Directory object class. The following values mostly used "user", "group" or "organizationalUnit" |
| baseDn | Active Directory container where user or group should be created. Its value should be absolute, containing Active Directory DC parts |
| relativeBaseDn | Active Directory container where user or group should be created. Its value should be relative to Active Directory DC parts. |
| cn | Object name |
| **System attribute** | **Description** |
|---|---|
| sAMAccontName | Is automatically mapped. It is internally mapped to role name or account name, without further customization |
| accountExpires | Sets the last date (in nanoseconds since 1600) in which the account will be valid. A common mapping expression is: ```Java if ( attributes {"expirationDate"} == null) return 9223372036854775807L; else return attributes{"expirationDate"}.getTime() * 10000L + 116445528000000000L; ``` |
| samAccountType | Can be used to identify distribution lists. A value of 268435457 or 268435456 means the AD group is a distribution list group rather than a security group. |
| lastLogon | The attribute can be used to get the last time an account was used. Soffid attribute is named **lastLogin** and the right mapping could be the following one. Mind when you make a reference to lastLogon attribute, every domain controller is queried about this attribute, as its value is not replicated across AD controllers: ```Java if ( lastLogon == null || lastLogon == void) return null; Long v = Long.decode(lastLogon); v = v / 10000000L; v-=11644473600L; return new Date(v*1000); => lastLogin ``` |
| userCannotChangePassword | true/false This is a virtual attribute that can be used to indicate if a user can or cannot change the password. You can't assign this permission by directly modifying the UserAccountControl attribute. |
For more information about how you may configure attribute mapping, see the following link: [Soffid Attribute Mapping Reference](https://bookstack.soffid.com/link/72#bkmrk-soffid-attributes)
For instance: [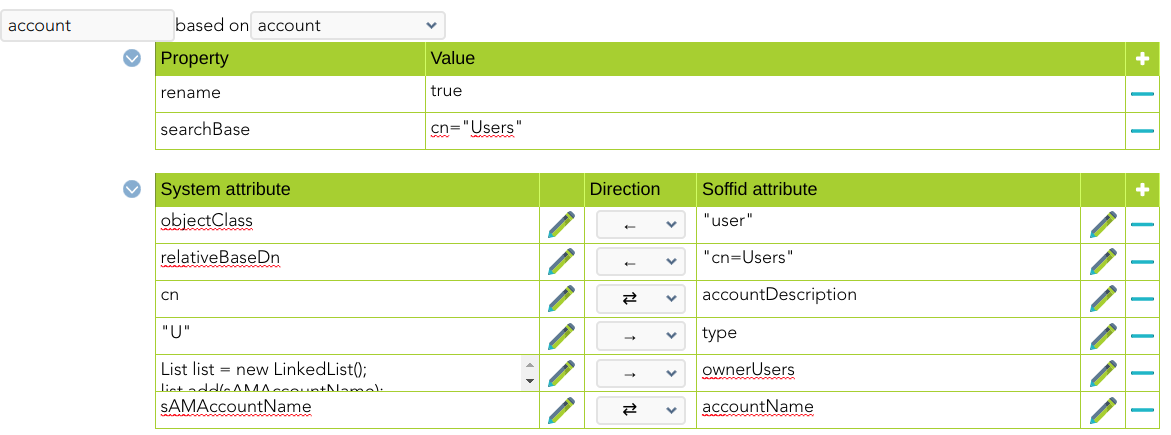](https://bookstack.soffid.com/uploads/images/gallery/2022-06/image-1654785419948.png) [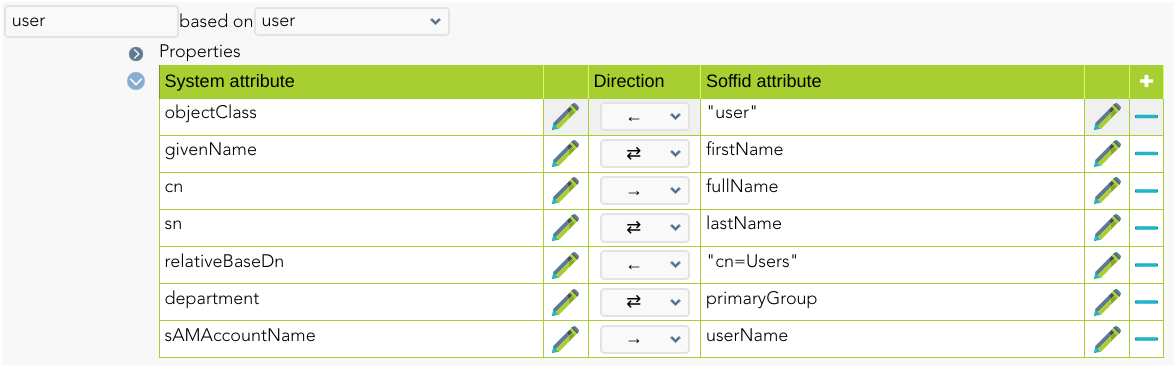](https://bookstack.soffid.com/uploads/images/gallery/2022-06/image-1654785472665.png) #### Triggers You can define BeanShell scripts that will be triggered when data is loaded into the target system (outgoing triggers). The trigger result will be a boolean value, true to continue or false to stop. Triggers can be used to validate or perform a specific action just before performing an operation or just after performing an operation on target objects.To view some examples, visit the [Outgoing triggers examples page](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors/page/outgoing-triggers-examples "Outgoing triggers examples").
## Avoid incremental load authoritative The Customizable Active Directory connector has an incremental load authoritative process. When this process is executed, it requests the changes to Active Directory after the **uSNChanged**. The value of this field is saved in Soffid in the parameter **soffid.sync.authoritative.change.NAME\_OF\_THE\_AGENT**If you want to launch a complete load authoritative process, remove this parameter first. At the end of the process, the parameter will be generated automatically.
For more information, go to the [Soffid Parameters page](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/soffid-parameters "Soffid parameters"). ## Password Rotation When you are configuring password rotation using Windows Connector, it could be necessary to make some changes in the local computar policies. The Local Computer Policies on the target Windows server mentioned below: - **User Account Control: Admin Approval Mode for Built-in Administrator Account** - **User Account Control: Run All Administrator in Admin Approval Mode** Need to be disabled for PAM application to connect target server and reset password of privilege accounts. If the Policies are originally in ‘Enabled’ mode, then after disabling them a system restart may required for the Policies to get applied on target servers properly. To check the User Access Policies on servers, follow below mentioned path: Open group policy editor **Run > gpedit.msc > Local Computer Policy > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options > select policy ‘User Account Control: Run all administrators in Admin Approval Mode’ and ‘User Account Control: Run All Administrator in Admin Approval Mode’ and select Disabled and apply > OK**.