# Shell Connector
## Introduction
### Description
Linux Connector could manage a lot of services running on Linux systems (either 32 or 64 bits).
### Managed System
This connector has implemented several ways to communicate with services on Linux, below, the list of those services:
- Shell
- SSH
- Cisco ASA
- Exchange
- Power Shell
If your system is not in the previous list, it's possible to include it easily!
For more information to check if your system may be synchronized with this connector you do not hesitate to contact us through our [Contact form](http://www.soffid.com/contactform/)
### Prerequisites
A Soffid Synchronization Server must be installed on the managed Linux system.
## Download and Install
This addon is located in the Connectors section and its name is **Shell Connector.**
For more information about the installation process you can visit the [Addons Getting started](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/addons-getting-started/page/getting-started "Addons installation") page.
## Agent Configuration
### Basic
#### Generic parameters
After the installation of the addon, you may create and configure agent instances.
To configure this Shell Connector you could select one agent, from the next list of available agents, in the attribute "Type" of the generic parameters section in the agents' page configuration.
- Shell Agent
- SSH Agent
- Cisco ASA Agent
- Exchange Agent
- Power Shell Agent
For more information about how you may configure the generic parameters of the agent, see the following link: [Agents configuration](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/agents "Agents")
#### Custom parameters
Below, there are the specific parameters for each agent implementation.
##### Shell Agent
| Shell
| Shell to assign to new users
|
| Persistent
| Two options \[ Yes , No \].
|
| Prompt
|
|
| Password hash algorithm
| For instance SHA1, SHA-256
|
| Password hash prefix
| For instance SHA
|
| Enable debug
| Two options: \[ Yes / No \]. When it is enabled more log traces are printed in the Synchronization Server log
|
##### SSH Agent
| User name
| User Linux for the SSH connection
|
| SSH Key file (optional)
|
|
| SSH Key (optional)
| |
| Password
| The password of the user Linux
|
| Server
| Host or IP of the server for the SSH connection
|
| Password hash algorithm
| For instance SHA1, SHA-256
|
| Password hash prefix
| For instance SHA
|
| Charset
| For instance: UTF-8
|
| Enable debug
| Two options: \[ Yes / No \]. When it is enabled more log traces are printed in the Synchronization Server log
|
| User name
| User Linux
|
| Key file (optional)
|
|
| Password
| The password of the user Linux
|
| Privileged password
|
|
| Server
| Host or IP of the server
|
| Charset
| For instance: UTF-8
|
| Enable debug
| Two options: \[ Yes / No \]. When it is enabled more log traces are printed in the Synchronization Server log
|
| User name
| Exchange user (with administrator permissions)
|
| Password
| The password of the exchange user
|
| Exchange server PS script (RemoteExchange.ps1 / exshell.psc1)
| For instance "E:\\Microsoft\\Exchange Server\\V15\\Bin\\exshell.psc1"
|
| Enable debug
| Two options: \[ Yes / No \]. When it is enabled more log traces are printed in the Synchronization Server log
|
| Exchange version
| Options: \[ 2007 | 2010+ \]
|
| Startup script
|
|
| Password hash algorithm
| For instance SHA1, SHA-256
|
| Password hash prefix
| For instance SHA
|
| Enable debug
| Two options: \[ Yes / No \]. When it is enabled more log traces are printed in the Synchronization Server log
|
| check
| fgrep $user /etc/passwd
|
| delete
| userdel $user
|
| insert
| useradd $user
|
| selectAll
| cat /etc/passwd
|
| selectAllParse
| (\[^:\]\*):\[^\\n\]\*
|
| selectByAccountName
| fgrep $user /etc/passwd
|
| selectByAccountNameParse
| (\[^:\]\*):\[^\\n\]\*
|
| update
| usermod $user
|
| updatePassword
| -
|
| validatePassword
| -
|
| check
| show run user $user
|
| checkAttributes
| user level
|
| checkParse
| username (\[^ \]+) password.\*privilege (\\d+)\\r\\n
|
| delete
| no username $user
|
| insert
| username $user password $password encrypted privilege $level
|
| selectAll
| show run user
|
| selectAllAttributes
| user level
|
| selectAllParse
| username (\[^ \]+) password.\*privilege (\\d+)\\r\\n
|
| selectByAccountName
| show run user
|
| selectByAccountNameParse
| username (\[^ \]+) password.\*privilege (\\d+)\\r\\n
|
| selectByAccountNamelAttributes
| user level
|
| update
| username $user password $password encrypted privilege $level
|
| updatePassword
| username $user password $password encrypted privilege $level
|
| check
| fgrep $user /etc/passwd
|
| delete
| userdel $user
|
| insert
| New-Mailbox -UserPrincipalName "${UserPrincipalName}" -Name "Shell plugin" -Alias "${Alias}" -Room
|
| selectAll
| Get-Mailbox
|
| selectByAccountName
| Get-Mailbox "Shell plugin"
|
| update
| usermod $user
|
| updatePassword
| -
|
| validatePassword
| -
|
| user
| accountName
|
| this{"1"}
| accountName
|
| level
| attributes{"level"}
|
| user
| accountName
|
| password
| password
|
For more information about how you may configure attribute mapping, see the following link: [Soffid Attribute Mapping Reference](https://bookstack.soffid.com/link/72#bkmrk-soffid-attributes)
For instance:
[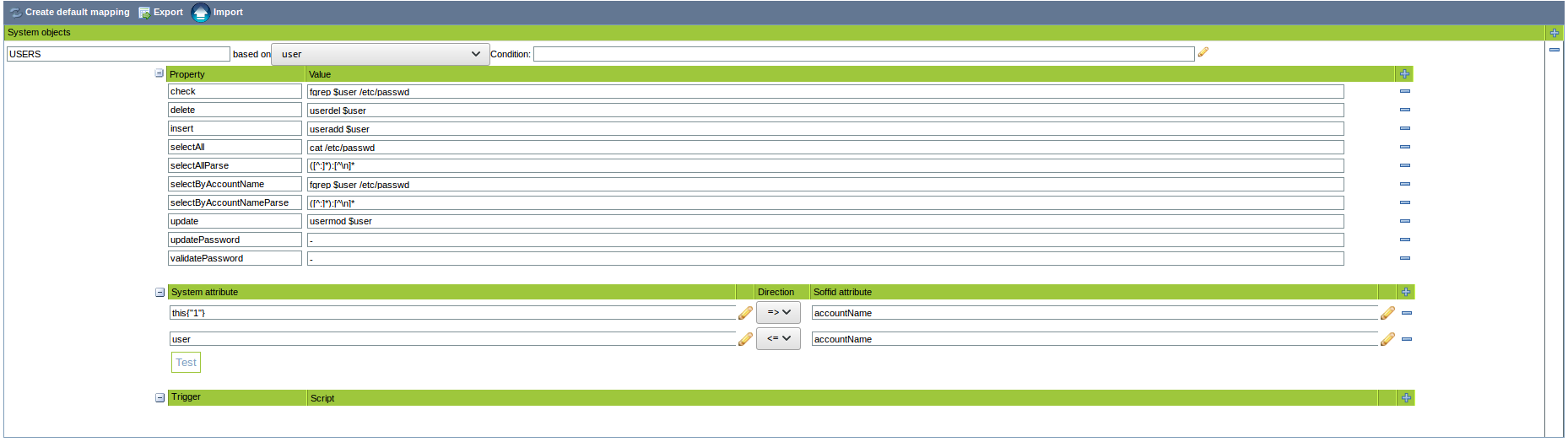](https://bookstack.soffid.com/uploads/images/gallery/2021-04/shell-connector-example.png)
#### Triggers
You can define BeanShell scripts that will be triggered when data is loaded into the target system (outgoing triggers). The trigger result will be a boolean value, true to continue or false to stop.
Triggers can be used to validate or perform a specific action just before performing an operation or just after performing an operation on target objects.
"Cisco ASA Agent" has not implemented this feature.
To view some examples, visit the [Outgoing triggers examples page](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors/page/outgoing-triggers-examples "Outgoing triggers examples").
### Load triggers
You can define BeanShell scripts that will be triggered when data is loaded into Soffid (incoming triggers). The trigger result will be a boolean value, true to continue or false to stop.
Triggers can be used to validate or perform a specific action just before performing an operation or just after performing an operation into Soffid objects.
To view some examples, visit the [Incoming triggers examples page.](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/connectors/page/incoming-triggers-examples "Incoming triggers examples")
### Account metadata
Agents allow you to create additional data, on the "Account metadata" tab, to customize the accounts created for that agent. This additional information will be loaded with the agent's information, or calculated as defined in the mappings.
The additional data can be used in both mappings and triggers.
The attributes which you define here will be shown when you click on the proper account, on the Accounts Tabs at user page.
## Operational
### Monitoring
After the agent configuration you could check in the monitoring page if the service is running in the Synchronization Server, please go to:
- Start Menu > Administration > Monitoring and reporting > Syscserver monitoring
### Tasks
#### Authoritative
If you are checked "Authorized identity source", an automatic task to load identities from the managed system to Soffid is available, please go to:
- Start Menu > Administration > Monitoring and reporting > Scheduled tasks
And you will something like "Import authoritative data from <AGENT\_NAME>".
#### Reconcile
If you are configured the "Attribute Mapping" tab with some of our objects: "user, account, role, group or grant", an automatic task to synchronize these objects from the managed system to Soffid is available, please go to:
- Start Menu > Administration > Monitoring and reporting > Scheduled tasks
And you will do something like "Reconcile all accounts from <AGENT\_NAME>".
### Synchronization
Regarding the synchronization of the objects, there are two possible options:
- If you are checked the generic attribute "Read Only" in the "Basics" tab, only the changes in the managed systems will be updated in Soffid. We recommend these options until the global configuration of Soffid will be tested.
- If you are not checked the generic attribute "Read Only" in the "Basics" tab, all the changes in Soffid or the managed system will be updated in the other. Note that this synchronization must be configured in the "Attribute mapping" tab correctly.
For more information about how you may configure the generic parameters of the agent, see the following link: [Agents configuration](https://bookstack.soffid.com/books/soffid-3-reference-guide/page/agents "Agents")